Fenugreek, scientifically known as Trigonella foenum-graecum, is an herb that belongs to the legume family. Fenugreek seeds are endowed with a distinct sweet smell like syrup or caramel. This aroma is due to the compound sotolon found in the seeds. Fenugreek is grown commercially in nations like India, Pakistan, Egypt or Morocco and affects global supply and demand. As a natural remedy for issues like indigestion and heartburn, it is frequently prepared into teas or added to dishes. The history of fenugreek is extensive and intricate entwined with numerous cultures and traditions. Let’s investigate Fenugreek’s historical and cultural tapestry.

Ancient Origins: Fenugreek’s ancient history spans Egypt, Greece and Mesopotamia. Greeks used it as animal fodder and in rituals.
Culinary Heritage: Fenugreek’s distinctive flavor and aroma made it a staple in various cuisines. Indian, Middle Eastern and North African dishes often incorporate fenugreek seeds or leaves.
In Indian cooking, fenugreek leaves (“methi”) are used in curries, while seeds are ground into spice blends (“masalas”) and added to pickles and chutneys.
Cultural Beliefs and Folklore: Fenugreek has historical value and varies in symbolism amongst cultures. It is incorporated into marriage and childbirth rites since it is connected to fertility. Because they believed it warded off evil spirits, the ancient Egyptians employed it in amulets.
Modern Research and Continuation: Its potential advantages for controlling blood sugar, heart health and other factors have been studied in depth. Despite technical improvements, fenugreek continues to be valued for its cultural and health-related significance maintaining its role in traditional rituals.
Nutritional Profile of Fenugreek
Here’s a glimpse into the nutritional profile of fenugreek:
Macronutrients
Protein: Fenugreek seeds are a great complement to vegetarian diets because they are a superior source of plant-based protein. The component accounts for 23% of the seed content. A fundamental food, protein serves a variety of purposes in the body including supporting the immune system and promoting tissue regeneration.
Carbohydrates: Fenugreek seeds contain carbohydrate including dietary fiber that improves digestive health and aid in blood sugar regulation. Carbohydrates make up 58% of the composition.
Micronutrients
Vitamins: One of the many vitamins that are plentiful and essential for both brain and metabolism function is vitamin B6. Vitamin C, an antioxidant that strengthens the immune system is also present.
Minerals: Fenugreek is notably high in minerals like iron, which is crucial for oxygen transport in the blood. It also contains magnesium, a mineral that is important for many of the chemical processes which include muscle and nervous system function.
Phytonutrients
Saponins: These compounds have been associated with potential health benefits, including immune support and cholesterol management.
Flavonoids: Fenugreek contains flavonoids, which possess antioxidant properties that help protect cells from oxidative stress.
Soluble Fiber: Fenugreek seeds have soluble fiber that is good for your heart, digestion and controlling blood sugar.
Amino Acids: Fenugreek seeds contain the amino acid tryptophan, which aids in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation.
Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids: Tiny amounts of these crucial fatty acids which help your heart and control inflammation are present in fenugreek seeds. It contains 6% fat Fat-soluble vitamins which are absorbed and stored along with healthy fats.
Caloric Value: Fenugreek seeds are relatively low in calories, making them a nutrient-dense addition to meals.
Antioxidants: Fenugreek contains antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress and protect cells from damage.
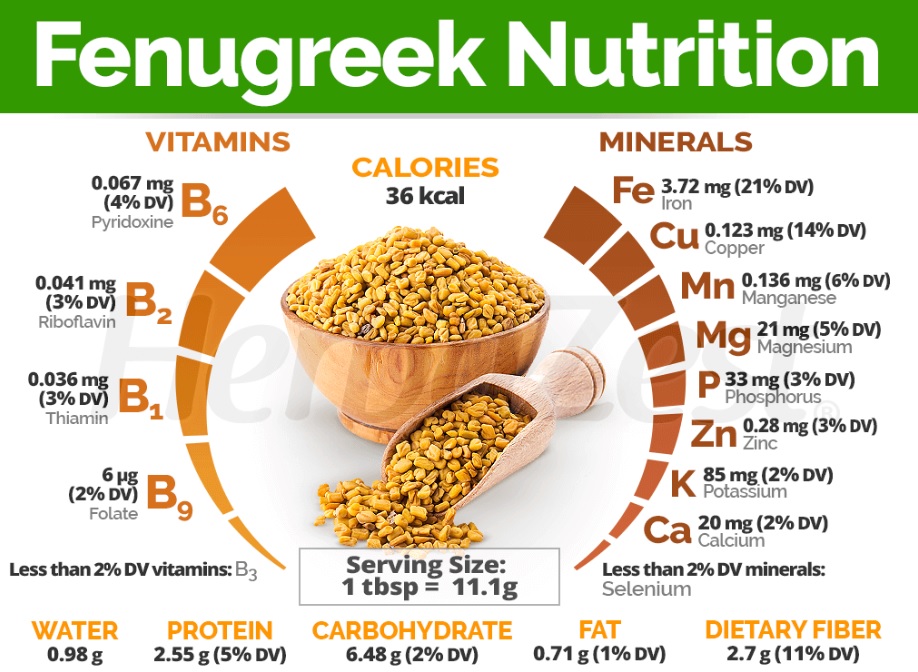
Nutritional Composition of Fenugreek Seeds (per 100 grams)
Fenugreek seeds provide 1,350 kilojoules (323 kcal) of energy per 100-gram serving. Fenugreek seeds contain 9% water. Fenugreek seeds contribute significantly to calcium intake, providing 40% of the Daily Value (DV). For strong bones, healthy muscles, and smooth nerve transmission, calcium is essential. Fenugreek seeds provide 59% of the Daily Value of manganese. Fenugreek seeds offer a substantial amount of iron, providing 262% of the Daily Value.
World Cuisines with Fenugreek: A Global Culinary Adventure
Fenugreek’s unique taste enhances global cuisines adding depth to dishes like tangy Ethiopian stews and fragrant Indian curries. Let’s take a gastronomic journey through fenugreek’s presence in various world cuisines:
- Indian Cuisine: Fenugreek (“methi” in Hindi) is a beloved ingredient in Indian kitchens. Fenugreek leaves are used in dishes like “methi paratha” (flatbread) and “methi thepla” (spiced flatbread). Fenugreek seeds are essential in spice blends and curries, adding a slightly bitter note and enhancing flavors.
- Middle Eastern Cuisine: Fenugreek seeds are a common ingredient in Middle Eastern cuisine. They’re used in spice mixes like “za’atar” and add complexity to stews and rice dishes.
- North African Cuisine: Fenugreek is a key component in North African spice blends like “berbere” and “ras el hanout.” It contributes to the distinctive flavors of dishes like “doro wat” (Ethiopian chicken stew) and “tagine” (slow-cooked Moroccan dish).
- Mediterranean Cuisine: Fenugreek seeds are used in Mediterranean breads and pastries. They also appear in Turkish and Greek Cuisine giving some dishes a slight bitterness.
- South Asian Cuisine: Fenugreek seeds and leaves are also utilized in Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi, and Pakistani food outside of India. Pickles, lentil recipes, and curries all benefit from the flavor of fenugreek.
- European Cuisine: In some European cuisine, especially Mediterranean recipes, fenugreek is used regularly. It’s likely to appear in Mediterranean salads, soups and spice blends.
- Caribbean Cuisine: Fenugreek may find its way into Caribbean cooking, especially in dishes with Indian influences.
- Global Fusion: Modern culinary exploration often combines fenugreek with other ingredients to create fusion dishes that bridge cultural divides.
Its position as a real global ingredient enriching dishes and connecting people with the joy of eating contributes to its ability to bring together different flavors and cultures.
Exploring Fenugreek’s Diverse Health Benefits
Digestive Health and Appetite Regulation
- Bitter Properties: Fenugreek’s bitterness stimulates the digestive system, aiding in the breakdown of food and alleviating discomforts like bloating and indigestion.
- Soluble Fiber: Fenugreek’s soluble fiber content promotes healthy digestion by softening stools and supporting regular bowel movements.
- Appetite Management: The fiber-rich nature of fenugreek can contribute to feelings of fullness, helping to manage appetite and prevent overeating.
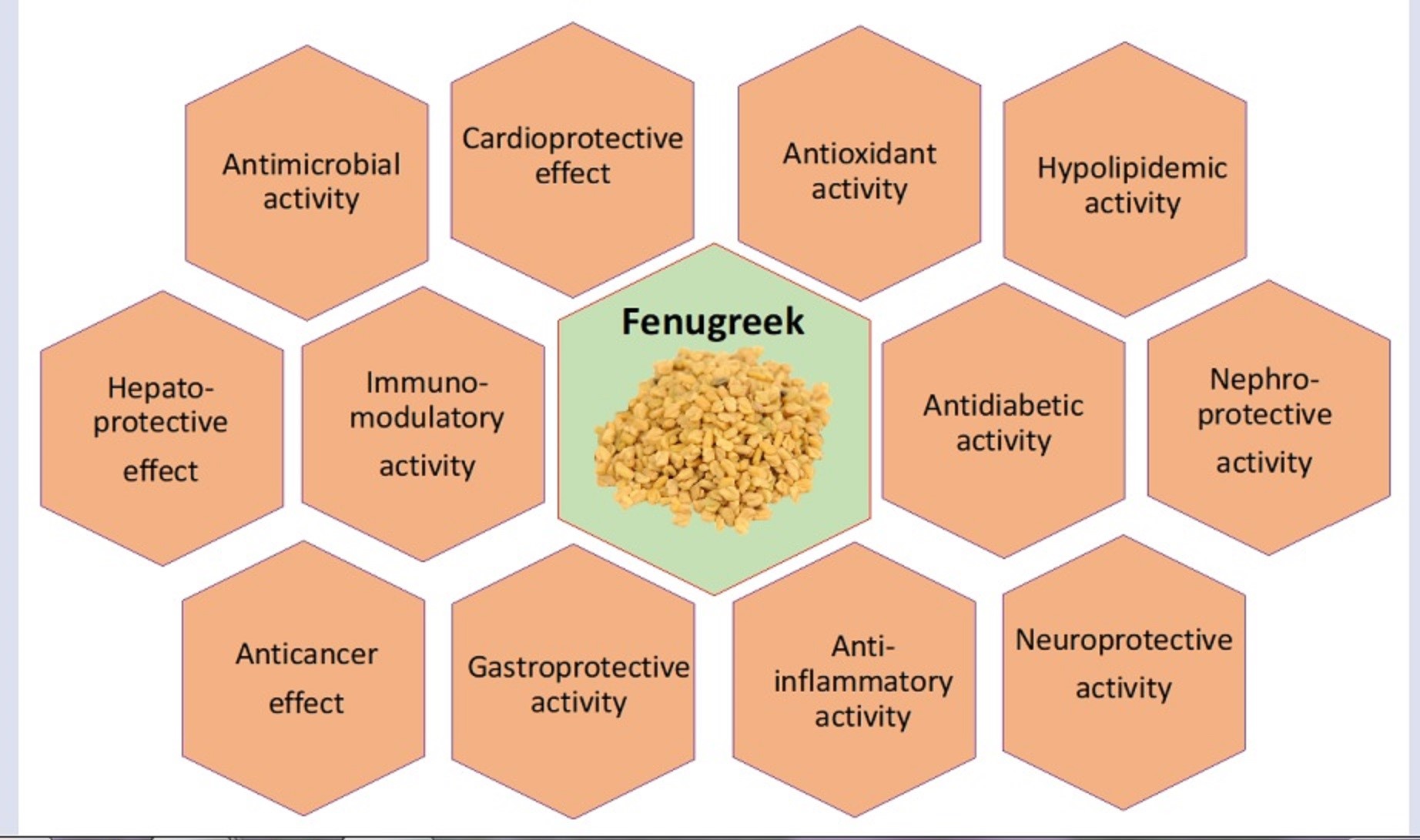
Blood Sugar Control and Diabetes Management
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Fenugreek’s soluble fiber, along with compounds like trigonelline, may help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of glucose.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Research suggests that fenugreek may enhance insulin sensitivity, contributing to better blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes.
Hormonal Balance and Women’s Health
- Hormonal Regulation: Fenugreek’s compounds have been associated with hormonal balance, particularly in women.
- Menstrual Comfort: Fenugreek’s traditional use includes easing discomfort during menstrual cycles, possibly due to its influence on hormonal fluctuations.
Impact on Cholesterol Levels
- Cholesterol Regulation: Fenugreek’s saponins have been linked to potential reductions in LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels.
Cardiovascular Benefits
- Blood Pressure Support: Some research suggests that fenugreek may aid in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels due to its potential to promote blood vessel relaxation.
- Heart Protection: Fenugreek’s combination of cholesterol management and blood pressure regulation can collectively contribute to overall heart health.
Aiding Weight Management
- Metabolic Influence: Fenugreek’s compounds may impact metabolism, potentially assisting in weight management by supporting efficient energy utilization.
- Appetite Regulation: The soluble fiber in fenugreek can promote feelings of fullness, potentially aiding in appetite control and weight maintenance.
Promoting Skin and Hair Health
- Skin Conditions: Fenugreek’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties may offer relief for certain skin issues when applied topically.
- Hair Care: Fenugreek’s protein and nutrient content make it a popular ingredient in hair masks and treatments to promote hair growth and shine.
Enhancing Milk Production
- Traditional Use: Fenugreek has been traditionally used by nursing mothers to boost milk production.
- Scientific Evidence: Some studies suggest that fenugreek may indeed have a positive impact on milk supply, though individual responses may vary.
Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
- Anti-inflammatory Potential: Compounds in fenugreek may help treat illnesses and discomfort brought on by inflammation.
- Antioxidant Properties: Fenugreek contains antioxidants that help neutralize harmful free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage.
Fenugreek: Allergies and Adverse Reactions
Although fenugreek offers potential health benefits, it should be used cautiously due to possible allergies and negative effects. Fenugreek can cause reactions in certain people, just like any herb or food.
Allergic Reactions
Pollen Allergies: Some individuals with pollen allergies, especially to plants like ragweed or birch, may experience cross-reactivity with fenugreek. These signs of allergies, such as coughing, sneezing and respiratory discomfort may appear.
Contact Dermatitis: Applying fenugreek topically can cause skin reactions in sensitive individuals, leading to redness, itching, or rash.

Gastrointestinal Distress
Bitter Taste: Fenugreek’s bitterness might not be well-tolerated by some individuals, leading to gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, or an upset stomach.
Gas and Bloating: Some people may experience gas and bloating due to the fiber content of fenugreek seeds especially if they ingest excessive amounts of it.
Allergic Reactions to Legumes
Cross-Allergenicity: If you’re sensitive to fenugreek, you might also have a higher chance of being allergic to legumes such as chickpeas or peanuts.
Consultation and Moderation
- Healthcare Provider: Before using fenugreek as a medicine, talk to your doctor if you have any allergies, illnesses or are on any medications.
- Moderation: As with any herb or supplement, moderation is key. Overconsumption of fenugreek, especially in supplement form, might lead to unwanted effects.
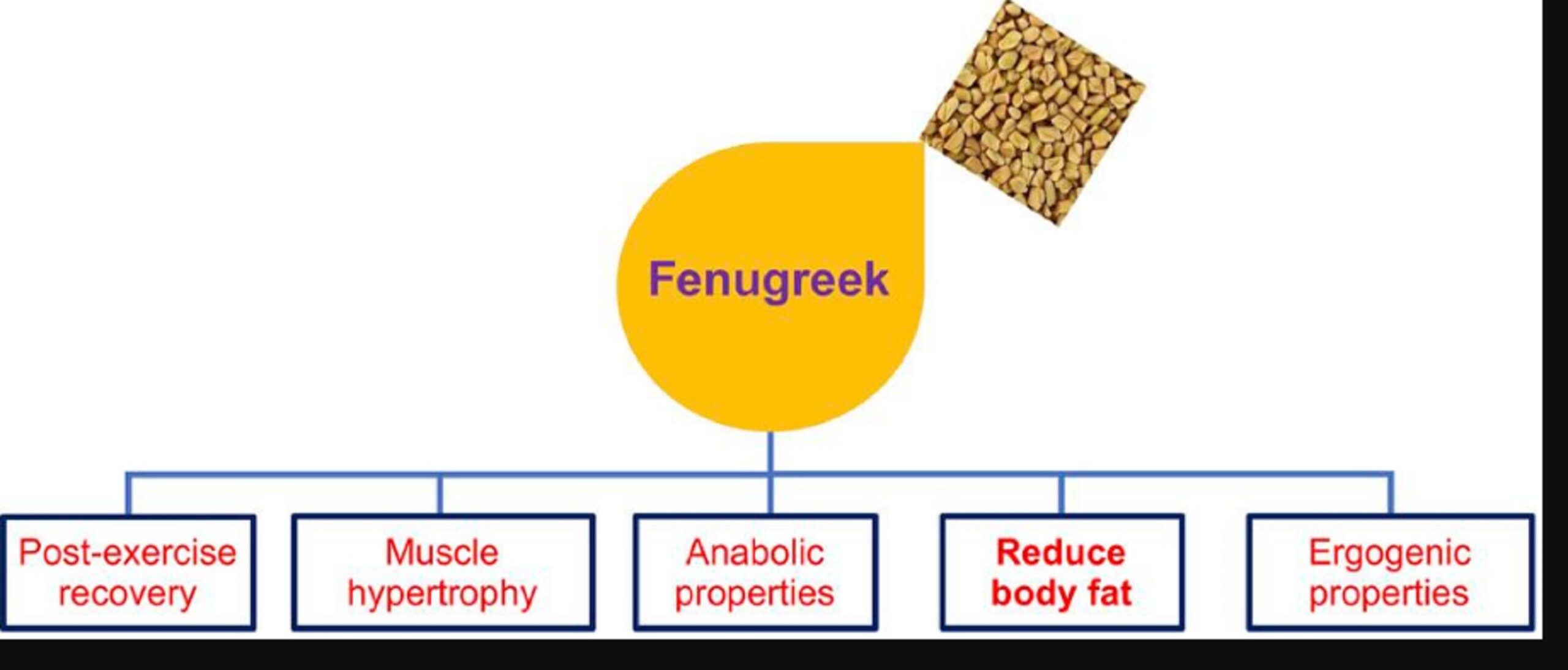
Fenugreek Supplements for Bodybuilding: Improving Fitness Objectives
- Testosterone and Muscle Growth: Fenugreek is often associated with its potential to support healthy testosterone levels, which are important for muscle development and overall fitness. Based on certain studies, the substances in fenugreek might support making proteins, which is important for building and fixing muscles.
- Gym Performance and Endurance: Fenugreek might help you have more energy during workouts and recover better afterward. This is accomplished by assisting your body’s defense mechanisms and improving bodily function.
- Fenugreek Supplements: Fenugreek is available in various forms; including capsules, tablets, and powders, often included in bodybuilding supplement formulations.
- Individual Variability: It’s important to note that individual responses to fenugreek supplementation may vary. Not everyone may experience the same level of benefits.
- Balanced Approach: While fenugreek pills could enhance a workout routine, they ought to be seen as a component of a balanced lifestyle that also includes good nutrition and exercise.
Exploring the Variety of Fenugreek-Based Products in the Market
The popularity of fenugreek’s potential health benefits has led to a diverse array of fenugreek-based products available in the market. From culinary delights to health supplements, here’s an overview of the different fenugreek-based products you can find:
Culinary Delights
- Widely used in cooking, fenugreek seeds add a unique bitterness and nutty flavor to curries, pickles, spice blends, and even bread.
- Fresh or dried fenugreek leaves are utilized in various dishes, including parathas, curries, and salads, adding a distinctive aroma and taste.
- Fenugreek seeds can be sprouted, offering a fresh and crunchy addition to salads and sandwiches.
Herbal Teas and Infusions
- Prepared by steeping fenugreek seeds in hot water, fenugreek tea is enjoyed for its potential digestive benefits and mild flavor.
Health Supplements
- You can find fenugreek supplements in simple capsule or tablet forms.
- Powdered fenugreek supplements can be easily mixed into beverages, smoothies, or foods.
Beauty and Personal Care
- Fenugreek’s potential benefits for hair health have led to the creation of hair masks, oils, and shampoos containing fenugreek extracts.
- Topical products with fenugreek extracts are explored for their potential anti-inflammatory and soothing properties.
Fenugreek-Infused Cooking Oils
- Infusing olive oil with fenugreek seeds imparts a delicate fenugreek flavor to cooking and salads.
Ensuring the Quality and Authenticity of Fenugreek Supplements
- Choose Reputable Brands: Opt for well-known and reputable brands that have a track record of producing quality supplements. Look for brands that follow good manufacturing practices (GMP) and have third-party certifications.
- Read Labels and Ingredients: Carefully read the product label to check for a clear list of ingredients and their amounts. Look for supplements that contain standardized fenugreek extracts with specified percentages of active compounds, such as saponins or fenugreek galactomannans.
- Check for Certifications: Look for certifications from independent organizations, such as NSF International, USP (United States Pharmacopeia), or ConsumerLab, which test and verify the quality of supplements.
- Research Ingredients: Familiarize yourself with the specific bioactive compounds in fenugreek that contribute to its potential benefits. This will help you understand what to look for in the supplement.
- Avoid Fillers and Additives: Choose supplements that have minimal or no added fillers, preservatives, or artificial additives.
- Beware of Unrealistic Claims: Be cautious of supplements that make extravagant claims or promises that seem too good to be true.
- Physical Appearance: The supplement’s physical characteristics such as color, texture and odour might occasionally shed light on its quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Dosage Considerations for Fenugreek: How Much is Safe and Effective?
The appropriate dosage of fenugreek can vary based on individual factors and intended use. For general health and culinary purposes, around 1-2 teaspoons of fenugreek seeds or 5-30 grams of fenugreek powder daily is commonly used.
What areas of health are currently being explored with fenugreek?
Current research on fenugreek explores its potential in sports performance, digestive health, hormone balance, anti-inflammatory properties and neurological issues.
Does taking fenugreek in detox regimens include any possible risks?
Yes, including fenugreek in detox regimens might carry risks. These include allergic reactions, interactions with blood sugar medications, digestive discomfort, effects on pregnancy and breastfeeding, medication interactions, and possible interference with thyroid function. Consulting a healthcare professional before using fenugreek in a detox regimen is advised to ensure safety.
How does Fenugreek taste and smell?
Fenugreek has a distinctive bitter taste and a strong, aromatic scent. Some describe its taste as similar to maple syrup.
How is Fenugreek used in cooking?
Fenugreek seeds and leaves are commonly used as a spice in various cuisines, adding flavor and aroma to dishes. Fenugreek leaves, also known as “methi,” are often used in Indian cooking.
Can Fenugreek be used for weight loss?
Some research suggests that fenugreek may help with weight management by promoting a feeling of fullness and supporting a healthy metabolism. It’s important to remember that no single herb or supplement is a substitute for a balanced diet and exercise.
Is Fenugreek suitable for everyone?
While fenugreek is generally safe for most people, individuals with allergies, diabetes, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and those taking medications should consult a healthcare professional before using fenugreek supplements.









