Testosterone, often called the “main guy hormone,” is a type of steroid hormone. It has a strong effect on both guys and girls. Along with dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and androstenedione, it is part of a hormone family called androgens. In sports, the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) says that the testosterone-to-epitestosterone (T/E) ratio in urine is usually 4:1. If it’s higher, it might signal someone’s not playing fair. Research even found that the amount of testosterone you have can make you either a risk-taker or a bit more cautious.
Also, a study in a journal called “Psychological Science” found something interesting: guys with more testosterone might like fancy luxury brands. Testosterone is like the architect of muscles, helping us build strength and keeping our bones sturdy. It’s not just about muscles and bones. It’s also the reason we feel those romantic vibes and for that spark we feel!
The History of Testosterone
In the late 1800s, a new field of science called endocrinology started growing. This helped scientists find out about testosterone. In 1849, Arnold Berthold’s work inspired other scientists to try things with animal testicle parts. One of these scientists, Charles-Édouard Brown-Séquard, experimented on himself and got mixed results. This got people curious about what testicles do.
Big Discoveries:
In the 1900s, we learned a lot more about testosterone. In the 1920s, two scientists, Frederick Banting and Charles Best, took a hormone from dog testicles. They named it “testosterone.” This led to more research about what testosterone does, like how it makes people develop adult features and affects muscles.
Surprising Facts About Testosterone Levels
- Morning Boost: When the sun comes up, testosterone levels rise around 30% from 4 a.m. to 8 a.m., getting us ready for the day.
- Win or Lose: Winning a contest can make testosterone go up by 20%, but if you lose, it might drop by 24%. It’s like a hormonal rollercoaster ride.
- Dad Mode: When guys become dads, their testosterone drops about 26%. This helps them be more caring and connected to their kids.
- Happy Laughter: A good laugh can raise testosterone by 10%, adding joy and good vibes to social moments.
- Music Magic: Listening to favorite tunes can boost testosterone by 25%. Music not only affects our mood but also our hormones!
- Love Chronicles: In the early days of love, testosterone goes down by 20%. This might be why the “honeymoon phase” feels so dreamy.
The Process of Testosterone Production in the Testes
Testosterone is like the boss of masculinity and is mainly made in guys’ testes and, to a smaller degree, in girls’ ovaries. It’s directed by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. They send messages to the testes (or ovaries) to start making testosterone.
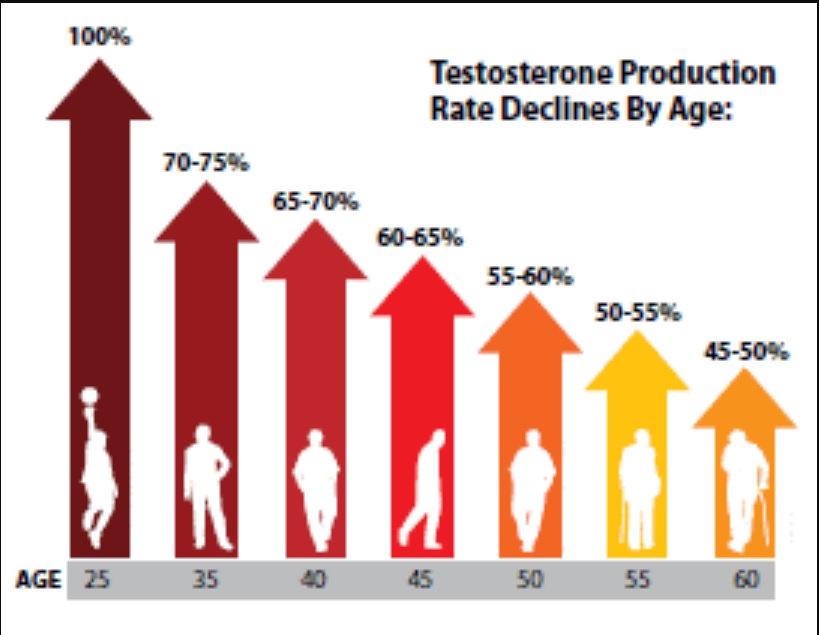
As we grow, our testosterone levels change. When we’re teenagers, our bodies kick production into high gear, causing all those changes like deep voices and growing hair. As we get older, the testosterone levels drop a bit.
We also have other hormones, like estrogen, which play a role too. They make sure everything stays balanced. If there’s too much or too little testosterone, it can affect how our bodies work and feel.
Low Testosterone (Hypogonadism)
Low testosterone, also known as hypogonadism, means your body isn’t making enough of this hormone. It can happen for various reasons, like aging, health conditions, or certain medications.
When testosterone levels take a dip, you might notice some changes. People could feel fatigue, reduced muscle mass, low energy, and even mood swings such as irritability and depression. can show up. Not to mention, your sex drive might not be as revved up as usual.
- Primary Hypogonadism: This is when the testes don’t make enough testosterone. Reasons might be genetics, infections, injuries, or immune issues.
- Secondary Hypogonadism: Here, the trouble starts in the brain’s control center, the hypothalamus or pituitary gland. They don’t send the right signals to the testes. It could be because of tumors, medications, or brain issues.
How it Affects You? Low testosterone can impact bone health and increase the risk of fractures. It can also affect your concentration and memory.

High Testosterone (Hyperandrogenism)
Hyperandrogenism is when there’s too much of a group of hormones called androgens in the body, including testosterone. This can happen because of health issues, genetics, or lifestyle influences.
- Too Much Androgens: Hyperandrogenism is when the body makes too many androgens. This can happen because of problems with the ovaries, adrenal glands, or tumors.
- How It Shows Up: Having too many androgens, especially testosterone, can cause issues with women such as more hair where it’s not usually found (like on the face), acne, messed-up periods, or even hair loss like guys. For men, it might not be very evident as they already have higher androgen levels.
- What It Can Do: Having too many androgens isn’t just about how you look. It can affect your body’s balance, especially many issues such as how your body handles insulin. Conditions like PCOS, which can affect periods and fertility, can be linked to too much androgen.
- Fixing the Issue: Treating hyperandrogenism depends on what’s causing it. For conditions like PCOS, lifestyle changes, birth control, or medicine that helps with insulin might be suggested. If there’s a tumor involved, doctors might need to do surgery or prescribe certain medicines.
- Getting Expert Help: Because hyperandrogenism is a bit tricky, an expert in hormones (endocrinologist) can help you with the right treatment plan for you.
Normal Ranges of Testosterone
Testosterone is different for everyone, but there are typical ranges that doctors use to determine if your testosterone levels are good.
- For Men: The normal range for total testosterone is usually around 300 to 1,000 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL). If your levels drop below 300 ng/dL, that might be a sign that something’s off.
- For Women: For adult women, the normal range is about 15 to 70 ng/dL. This might sound low compared to guys, but it’s important for things like bone health and mood.
- Age Matters: As you get older, your testosterone levels naturally dip a bit. It’s like your body’s way of adjusting to different stages of life. But if you’re on the lower end of the range and feeling symptoms such as low energy or mood changes, it’s worth checking in with a doctor.
- Personal Variations: Remember, these ranges are just general guidelines. What’s “normal” for you might be a bit different from someone else. It’s all about finding the balance that works best for your body.

Testosterone and Physical Performance
- Boosting Strength and Muscles: Testosterone helps our muscles grow stronger. It’s like giving them a signal to get bigger and more powerful. So, people with higher testosterone often have more muscle strength.
- Oxygen Power: This hormone can make our bodies produce more red blood cells which carry oxygen and give us energy. So, with more oxygen, we can go longer and feel less tired during physical activities.
- Metabolism Magic: Testosterone can also help our bodies use energy better. It helps our cells take in nutrients and use them efficiently. These are important activities such as running, jumping, and lifting weights.
- Recovery and Bouncing Back: After a tough workout, our bodies need to heal and get stronger. Testosterone helps speed up this recovery process. It reduces muscle damage and inflammation, which means we can get back to our activities faster.
- Everyone’s Included: Men usually have more testosterone, but women also have it in smaller amounts. It still helps both genders perform better in sports and exercise.
- Playing Fair: In sports, using extra testosterone or other substances to perform better isn’t fair play. Various organizations have rules to keep competition fair and honest.
Testosterone and Health
Testosterone is not just about manliness but is a multi-tasker for your health. Check out these important things it does:
- Strong Muscles and Bones: Testosterone helps muscles and bones stay healthy. It keeps bones strong and muscles growing.
- Body Fat and Metabolism: It also affects how your body uses fat and how it’s spread. If testosterone is low, you might gain belly fat.
- Heart Health: Your heart’s a fan of testosterone too. It helps make blood cells and keeps your blood vessels healthy, which is super important for your heart.
- Sleep and Immunity: Sleep and testosterone are buddies. If your sleep is not good, it might affect your testosterone and your overall health. And while the connection with the immune system is tricky, some studies say balanced testosterone could be good for your immunity.
- Sexual Health: For men, testosterone It’s responsible for your libido, sperm production and even the strength of your erections. For women, it helps keeps their desire alive and contributes to a healthy intimate life. Testosterone also affects your mood and how you feel about yourself, which can have a big impact on your romantic relationships. Imbalanced testosterone can also cause infertility.
Testosterone Levels Across the Lifespan:
- In the wild teen years, testosterone shoots up like a rocket, hitting its peak – around 700 ng/dL in guys. It’s what makes voices deepen and sparks those incredible growth spurts.
- Early adulthood keeps the energy flowing, with testosterone around 500-700 ng/dL, keeping you feeling alive and strong.
- Around your 40s, it starts to wave goodbye, dropping about 1% each year. Don’t worry, though! You’ll still have around 300-400 ng/dL, keeping your system functioning.
- As you get older and toward your 70s, testosterone slowly drops more – about 200-300 ng/dL.
Lifestyle and Testosterone: Diet, Exercise, and Stress Management
- Food is a friend: Have a balanced diet with zinc, vitamin D, and omega-3s for happy testosterone levels.
- Zinc power: Foods such as oysters, nuts, and lean meats have zinc that helps make testosterone.
- Sun and Vitamin D: Get sunlight and take fish, dairy, and eggs for great testosterone levels.
- Good fats matter: Avocado, nuts, and olive oil are like hormone helpers.
- Move it: Exercise, especially weight training, and intense workouts, can boost testosterone.
- Stay fit: Maintaining a healthy weight keeps hormones balanced – too much fat can mess things up.
- Stress less: Stress makes cortisol go up, which isn’t good for testosterone. Relax with meditation and yoga.
- Easy with drinks: Don’t drink too much – lots of alcohol can lower testosterone.
- Not too much exercise: Overdoing workouts without rest can drop testosterone for a bit. Give your body time to recover.

Health Problems that affect Testosterone Level
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can lead to lower testosterone levels. It’s like a loop – low testosterone can contribute to weight gain, and excess weight can lower testosterone.
- Diabetes matters: Diabetes, especially type 2, can affect your testosterone levels. High blood sugar and insulin resistance can impact hormone production.
- Chronic illness: Certain chronic illnesses, like kidney or liver disease, can impact how your body produces and uses hormones.
- HIV/AIDS: The virus and meds can throw off hormones.
- Pituitary problems: Issues with the pituitary gland can disrupt the signals that control testosterone production.
- Thyroid talk: Thyroid problems, like hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid), can throw off the balance of hormones in your body, including testosterone.
- Medications: Some medications, like certain painkillers and steroids, can interfere with testosterone production.
- Stress: High-stress levels can affect hormone production, including testosterone. It’s like a chain reaction in your body.
- Certain Cancers: Some cancers such as prostate cancer, or those affecting the testes, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland, can affect testosterone levels.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Some autoimmune diseases, like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, can impact hormone balance.
Remember, taking care of your testosterone involves good habits and understanding your body’s signals!
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): Considerations
- Getting the Right Diagnosis: Before you start TRT, it’s very important to figure out if low testosterone is the issue. Your doctor will talk to you about your symptoms and run some tests.
- Good and Not-so-Good Stuff: TRT can make you feel better – more energy, better mood, stronger muscles. But you need to watch out for things such as acne, sleep issues, and even changes in your blood cholesterol.
- It’s Personal: TRT isn’t the same for everyone. What works for one person might not be right for another. Your doctor will make a plan that fits your needs and health history.
- Keep Checking In: Once you’re on TRT, you’ll need to see your doctor regularly. They’ll check your testosterone levels and see how your body reacts. This helps make sure everything is fine.
- Long-Term: Starting TRT is like a commitment. Suddenly stopping can mess with your testosterone levels and how you feel. So, if you’re considering it, be ready for the journey.
Testosterone Hormone-Related Disorders
If testosterone levels go haywire – it can cause hormone troubles which can affect you in many ways.
- Klinefelter Syndrome: This genetic condition causes an extra X chromosome in males, affecting testosterone production and development. It can cause infertility, low energy, late puberty, smaller testes, and less facial hair.
- Trouble in the Testes: Sometimes, injuries, infections, or tumors can also affect testosterone levels. It can upset the hormone balance. The testicle inflammation (orchitis) or testicular cancer can also occur.
- Andropause: Sometimes called “male menopause,” this is when testosterone levels drop as men age. It can cause fatigue, mood swings, and a decrease in libido.
- Testicular Disorders: Problems with the testes, like tumors or injury, can mess with testosterone production. This can affect fertility and overall health.
- Anabolic Steroid Abuse: Using steroids that mimic testosterone can lead to hormonal imbalance. This can cause various health problems, including mood swings and damage to organs.
- Hyperthyroidism: An overactive thyroid can affect testosterone levels. Thyroid issues can affect the entire hormone system.
- Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH): This genetic disorder can cause the adrenal glands to produce too much androgen, which can cause irregular periods and excess hair in women.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): While often thought of as a women’s issue, PCOS can also cause elevated testosterone levels in women. This can lead to irregular periods, hirsutism (excessive hair growth), and other symptoms.
Prescription Testosterone Gels and Patches
- Skin Gels and Patches: These are creams or stickers you put on your skin to get the right amount of testosterone. They help people with low testosterone, especially those with hypogonadism.
- Injections: People get these shots every few weeks to keep their levels balanced.
- Pellets: These are little things placed under your skin, usually in your hip area. They slowly release testosterone for a few months.
- Natural Boosters: Some use natural herbs such as fenugreek, ashwagandha, and Tongkat Ali to help their testosterone levels.
- Anabolic Steroids: Some use these to get stronger muscles for sports. But, using them for non-medical reasons can be risky and against the law.
- Clomiphene Citrate: This medicine helps your body make more testosterone naturally.
- DHEA Supplements: These are pills that might help make more testosterone from another hormone.
Busting Common Myths About Testosterone
Myth: Testosterone Supplements Are Magic Pills.
Reality: These supplements aren’t magic fixes. If you take them without a doctor’s help, things could get messed up. Being healthy is more important.
Myth: Aging Means Low Testosterone.
Reality: Getting older doesn’t always mean low testosterone.
Myth: Testosterone Is Only About Sex Drive.
Reality: Testosterone isn’t just for wanting to get intimate. It also helps with helps with your energy level, strong bones and how you feel.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is andropause like menopause for women?
Andropause is kind of like menopause for men, but they’re not the same. Menopause is when women’s estrogen levels drop a lot, and they stop having periods. Andropause is when guys’ testosterone levels slowly go down as they get older, usually in their 40s or 50s.
Where can people find help with gender identity and hormone therapy?
Doctors, mental health support, LGBTQ+ groups, and community places are good spaces to get support for understanding your gender and hormones.
Are there ways to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) besides testosterone therapy?
Yep, there are different ways depending on the cause. In some cases, certain medicines, therapy, taking care of heart health and lifestyle changes might help.
How do they check testosterone levels?
To check testosterone levels, your doctor may order a blood test, usually in the morning, to measure your total and free testosterone levels. Based on the results, the doctor will determine if your levels are within a healthy range and discuss any necessary treatments.
Can testosterone therapy be undone?
Yes, testosterone therapy can be stopped or adjusted if needed. If you decide to discontinue testosterone therapy, your doctor will work with you to gradually reduce the treatment to prevent sudden hormone imbalances. It’s important to follow your doctor’s guidance to ensure a smooth transition.
Does low testosterone increase the risk of certain cancers?
The connection between low testosterone and the risk of specific cancers, like prostate cancer, is still being studied. While some research suggests a potential link, it’s not fully understood and is influenced by various factors. If you’re worried about this, talking to a healthcare professional can provide personalized insights based on your health situation.










