In a world full of hectic schedules and constant demands, the power of workouts to transform lives is nothing short of remarkable. Beyond the pursuit of physical fitness, workouts have the potential to impact us on a profound and holistic level. They extend their influence far beyond the confines of the gym, infiltrating our daily routines, mental well-being, and overall quality of life.
Yet, it doesn’t stop there. Workouts provide a platform for personal growth, self-discovery, and the cultivation of discipline and determination. In essence, workouts offer a gateway to a more vibrant, empowered, and fulfilled life.
So, whether you’re already an exercise enthusiast or someone considering a new fitness journey – the path to transformation is accessible to all, regardless of age, fitness level, or past experiences. It’s a path that begins with a single step, a first workout, and a commitment to your well-being.
Workout Routine
- Choose Your Workout Type: Decide on the type of exercise that aligns with your goals and interests. Options include cardio (e.g., running, cycling), strength training (e.g., weightlifting, bodyweight exercises), flexibility (e.g., stretching), or a combination of these.
- Create a Workout Plan: Develop a structured plan that outlines the exercises, frequency, duration, and intensity of your workouts.
- Warm-Up: Before starting your main workout, engage in a warm-up routine to prepare your body. This may include light cardio (e.g., jogging in place), dynamic stretches, or mobility exercises.
- Maintain Proper Form: Focus on proper exercise form and technique to maximize effectiveness and minimize the risk of injury. If you’re unsure about form, consider working with a fitness trainer or watching instructional videos.
- Cool Down: After completing your main workout, engage in a cool-down routine that includes static stretching to improve flexibility and reduce post-exercise muscle soreness.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is key to achieving your fitness goals. Aim to stick to your workout schedule and make exercise a regular part of your routine.
- Rest and Recovery: Allow your body time to recover between workouts. Rest is essential for muscle repair and overall recovery. Overtraining can lead to injury and burnout.

Physical Changes with Workout
- Muscle Growth (Hypertrophy): Strength training and resistance exercises, such as weightlifting, can stimulate muscle growth. Over time, this leads to increased muscle size and definition.
- Fat Loss: Combining cardiovascular workouts (like running or cycling) with a calorie-controlled diet can lead to fat loss. Exercise helps burn calories and contributes to a reduction in body fat percentage.
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: Cardiovascular exercises, such as jogging, swimming, or brisk walking, can improve heart health by increasing the efficiency of the heart and circulatory system.
- Increased Strength and Endurance: Strength training and resistance exercises enhance muscular strength and endurance, making everyday activities easier to perform.
- Better Posture: Strengthening the core muscles can improve posture and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal problems.
- Improved Balance and Coordination: Regular workouts can enhance balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
- Reduction in Chronic Health Conditions: Exercise can help manage or prevent chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain cardiovascular diseases.
- Enhanced Immune Function: Regular physical activity can boost the immune system, making you less susceptible to illnesses.
- Increased Energy Levels: Regular exercise can lead to increased energy and reduced feelings of fatigue.
- Stress Reduction: Physical activity stimulates the release of endorphins, which are natural mood lifters that can reduce stress and anxiety.
- Change in Body Composition: With consistent exercise, you may experience changes in body composition, even if the scale doesn’t show significant weight loss. This can include reductions in body fat and increases in lean muscle mass.
- Increased Metabolic Rate: Muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue, so increasing muscle mass through exercise can lead to a higher resting metabolic rate.

What Science Says About Workouts and Fat Loss
- A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition compared different exercise regimens and found that participants who engaged in both aerobic and resistance training lost more body fat compared to those who did either exercise alone or remained sedentary.
- Another research published in the journal Obesity demonstrated that a combination of aerobic exercise and calorie restriction resulted in more significant fat loss than calorie restriction alone.
- The fundamental principle of fat loss is creating a calorie deficit, where you burn more calories than you consume. Scientific studies confirm that workouts contribute significantly to calorie expenditure. The more intense and prolonged the exercise, the greater the calorie burn. For instance, a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workout can elevate your post-exercise calorie burn, known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), for hours after your session ends.
- Muscle tissue plays a pivotal role in fat loss. Scientific research underscores that muscle is metabolically active, meaning it burns calories even at rest. When you engage in strength training workouts, you stimulate muscle growth (hypertrophy). As your muscle mass increases, so does your resting metabolic rate. In essence, you become a more efficient calorie-burning machine.
- During aerobic workouts, such as running or cycling, your body taps into its fat stores for energy. This process, known as fat oxidation, is well-documented in exercise physiology. Moderate-intensity cardio workouts are particularly effective at promoting fat utilization for energy. Over time, this contributes to a reduction in body fat percentage.
- A study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology investigated fat oxidation during exercise. It found that during aerobic workouts, the body relies on stored fat as a primary energy source, supporting the concept of fat loss through exercise.
- Exercise influences appetite-regulating hormones. Research suggests that some people experience reduced appetite after workouts. This appetite suppression can help with calorie control and weight management.
- While not directly related to fat loss, the psychological benefits of exercise are scientifically validated. Regular workouts have been shown to reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance self-esteem. These positive effects can influence your relationship with food and your ability to adhere to a calorie-controlled diet.
- Scientific evidence confirms that workouts are a critical component of a successful fat loss journey. However, it’s important to emphasize that exercise alone may not yield optimal results. Nutrition, sleep, and lifestyle factors also play significant roles. A holistic approach that combines a balanced diet with regular workouts is most effective for achieving and maintaining fat loss goals.
Workout Motivation: Setting Goals and Reinforcements for Success
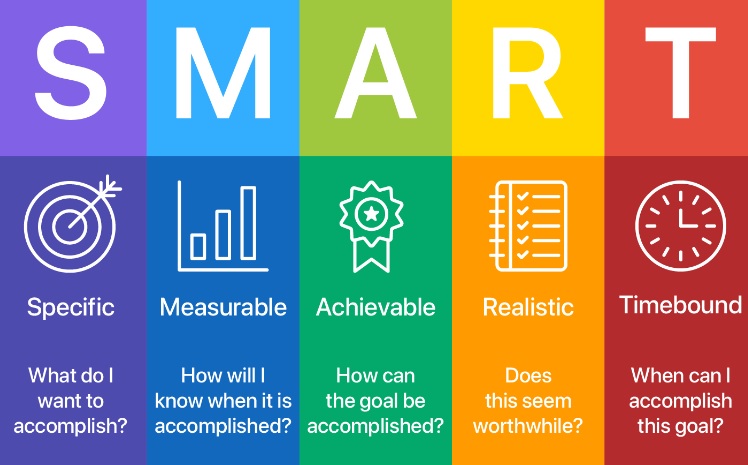
- Specific Goals: Make your workout goals specific and well-defined. For example, instead of a vague goal like “get fit,” set a specific goal like “run a 5K in under 30 minutes” or “lose 10 pounds in three months.”
- Measurable Goals: Goals should be measurable so you can track your progress. Use metrics like weight, body measurements, or fitness performance to measure success.
- Time-Bound Goals: Set deadlines for your goals to create a sense of urgency. For instance, aim to achieve a certain weight or complete a fitness challenge by a specific date.
- Short-Term and Long-Term Goals: Have both short-term and long-term goals. Short-term goals provide a sense of accomplishment, while long-term goals keep you focused on the bigger picture.
Positive Reinforcements
- Rewards: Establish a reward system for reaching milestones. Treat yourself to something you enjoy when you achieve a goal, whether it’s a new workout outfit or a favorite meal.
- Positive Self-Talk: Replace negative thoughts with positive affirmations. Remind yourself of your achievements and capabilities.
- Visualize Success: Close your eyes and visualize yourself accomplishing your fitness goals. Feel the sense of achievement and satisfaction.
- Celebrate Consistency: Acknowledge the importance of showing up and being consistent with your workouts. Even on days when motivation is low, celebrate the act of doing the workout.
- Accountability Partner: Partner with a friend or workout buddy who can hold you accountable and provide motivation on challenging days.
- Progress Photos: Take before-and-after photos to visually track your transformation. Seeing physical changes can be a powerful reinforcement.
- Mini-Celebrations: Celebrate small victories along the way. Whether it’s completing a challenging workout or sticking to a healthy meal plan, acknowledge your achievements.
Starting With Leg Workouts: Maximizing Your Lower Body Strength
- Balance and Stability: Leg workouts improve balance and stability, reducing the risk of falls and injuries, especially as you age.
- Metabolic Benefits: Lower body exercises engage large muscle groups, leading to an increased metabolic rate. This can aid in fat loss and weight management.
- Athletic Performance: Athletes rely heavily on powerful leg muscles for speed, agility, and explosiveness. Leg training can enhance athletic performance in various sports.
- Injury Prevention: A strong lower body can help prevent injuries, particularly in the knees and lower back, by providing better support and joint stability.
Key Leg Exercises
- Leg Curls and Extensions: These isolation exercises target the hamstrings (leg curls) and quadriceps (leg extensions). They are valuable for sculpting and strengthening specific leg muscles.
- Squats: Squats are the cornerstone of leg workouts. They target the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. Variations like goblet squats, front squats, and Bulgarian split squats add variety to your routine.
- Deadlifts: Deadlifts work the hamstrings, glutes, lower back, and core. They are excellent for building overall lower body strength and functional power.
- Lunges: Lunges help improve balance and target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Forward, reverse, and lateral lunges can be incorporated.
- Leg Press: The leg press machine is effective for isolating the leg muscles. It’s especially beneficial for those who may have limitations with free weight exercises.
- Step-Ups: Step-ups work the quadriceps and glutes while also improving balance and stability. You can use a bench or step platform for this exercise.

Incorporating Cardio Exercises Into Your Workout
- Incorporating cardiovascular exercise into your workout routine is essential for improving cardiovascular health, burning calories, and increasing overall fitness.
- Select cardiovascular exercises that you find enjoyable and sustainable. This could include activities like running, cycling, swimming, brisk walking, dancing, or even playing sports.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, as recommended by health guidelines. You can break this into manageable sessions throughout the week.
- Incorporate a variety of cardio activities to keep your workouts interesting and to engage different muscle groups. This can also prevent boredom and overuse injuries.
- Include a mix of low, moderate, and high-intensity cardio workouts. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) can be particularly effective for calorie burning and cardiovascular fitness.

Importance of Nutrition
- Nutrition plays a fundamental role in both workout performance and fat loss. Proper nutrition provides the body with the necessary fuel, nutrients, and support for exercise, recovery, and achieving weight management goals.
- Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy, especially during high-intensity workouts. Consuming an adequate amount of carbs ensures that you have the energy needed to perform at your best during exercise.
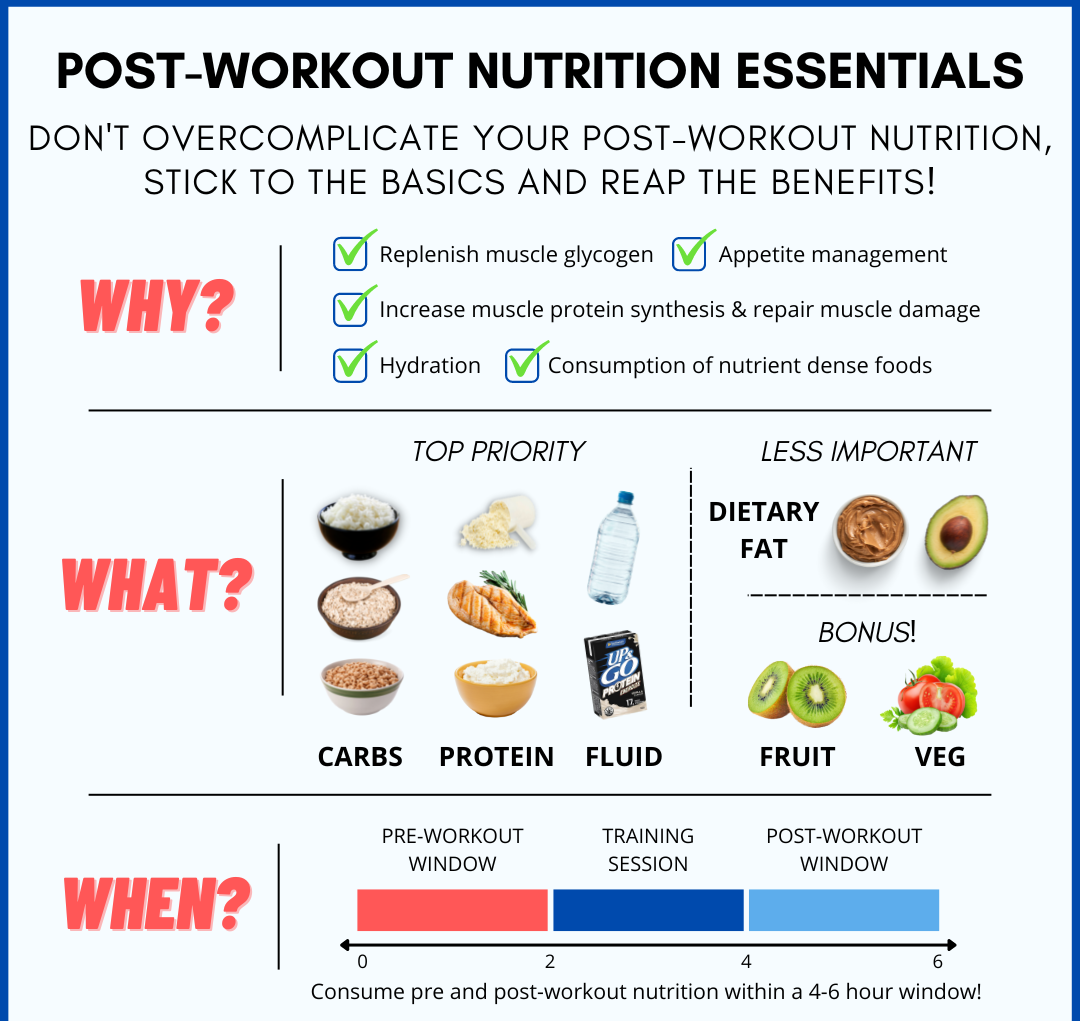
- After a workout, the body needs protein to repair muscle tissue and build new muscle. Adequate protein intake also helps prevent muscle loss when in a calorie deficit for fat loss.
- Dehydration can lead to reduced endurance, strength, and overall workout performance. Proper fluid intake ensures optimal hydration during workouts.
- A balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats supports overall health and workout performance. Each macronutrient serves specific roles in the body, and achieving the right balance helps maintain energy levels and support metabolism.
- To achieve fat loss goals, it’s essential to create a calorie deficit by burning more calories than you consume. Proper nutrition allows you to control calorie intake while still providing the necessary nutrients for workouts and overall health.
- When losing weight, the goal is to lose fat while preserving lean muscle mass. Adequate protein intake and proper nutrition help prevent muscle loss, ensuring that most of the weight lost comes from fat.
- Proper timing of meals and snacks around workouts can impact performance and recovery. Pre-workout meals provide energy, while post-workout nutrition aids in muscle recovery and glycogen replenishment.
- Sustainable, long-term fat loss and fitness progress depend on establishing healthy eating habits. A balanced and nutritious diet supports consistency and adherence to your fitness plan.









