HDL particles are tiny and dense with more protein compared to LDL and other lipoproteins. HDL particles are smaller and denser containing more protein than LDL (Low-density Lipoproteins). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular disease is the leading global cause of mortality.
In 2019, approximately 17.9 million people died from cardiovascular diseases accounting for 32% of all global deaths. The prevalence of heart disease varies across regions and countries. HDL cholesterol is called “good cholesterol” because it protects the heart. According to studies, the risk of heart disease is reduced by roughly 2-3% for every 1 mg/dL increase in HDL cholesterol. In some areas, especially where people follow a Mediterranean diet, higher HDL levels are common which might contribute to their rates of heart disease.
According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) between 2011 and 2014, 18% of individuals in the United States have low HDL cholesterol levels (levels less than 40 mg/dL for males and less than 50 mg/dL for women). Extensive research indicates that exercise has a beneficial impact on HDL levels with numerous studies showing a remarkable 20 % increase in HDL levels.
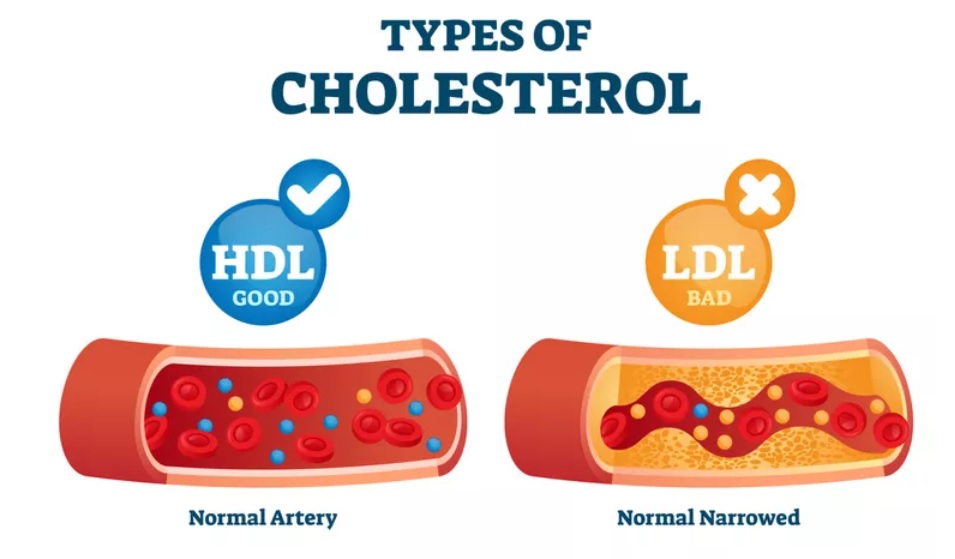
Overview of Cholesterol Types
Cholesterol, a lipid found in the blood and cells, serves essential functions in the body. Excessive cholesterol, especially specific types can be detrimental to your health.
There are two main types of cholesterol:
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein):
- Extra cholesterol from the bloodstream is sent by HDL to the liver, where it is processed before being eliminated from the body.
- A higher level of HDL is linked to a lower risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
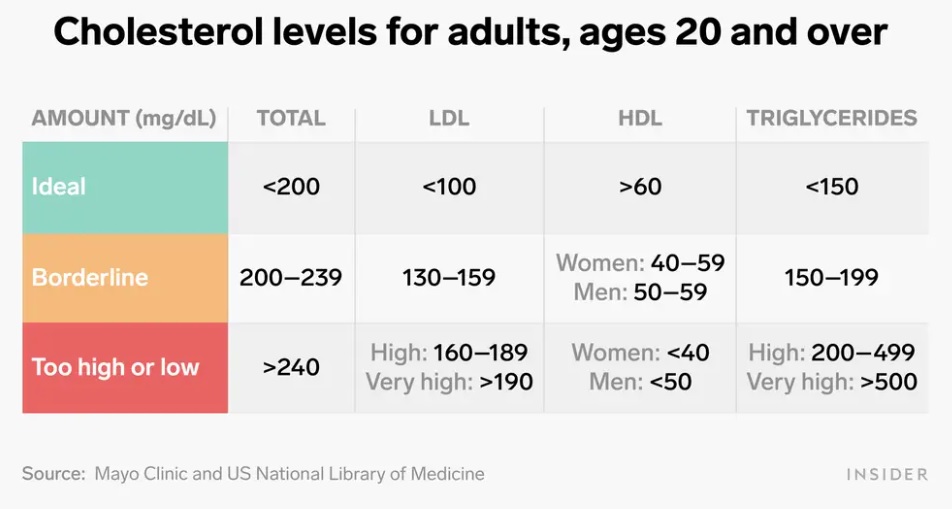
- For men, normal HDL cholesterol levels are generally considered to be 40 mg/dL or higher while for women, they are 50 mg/dL or higher.
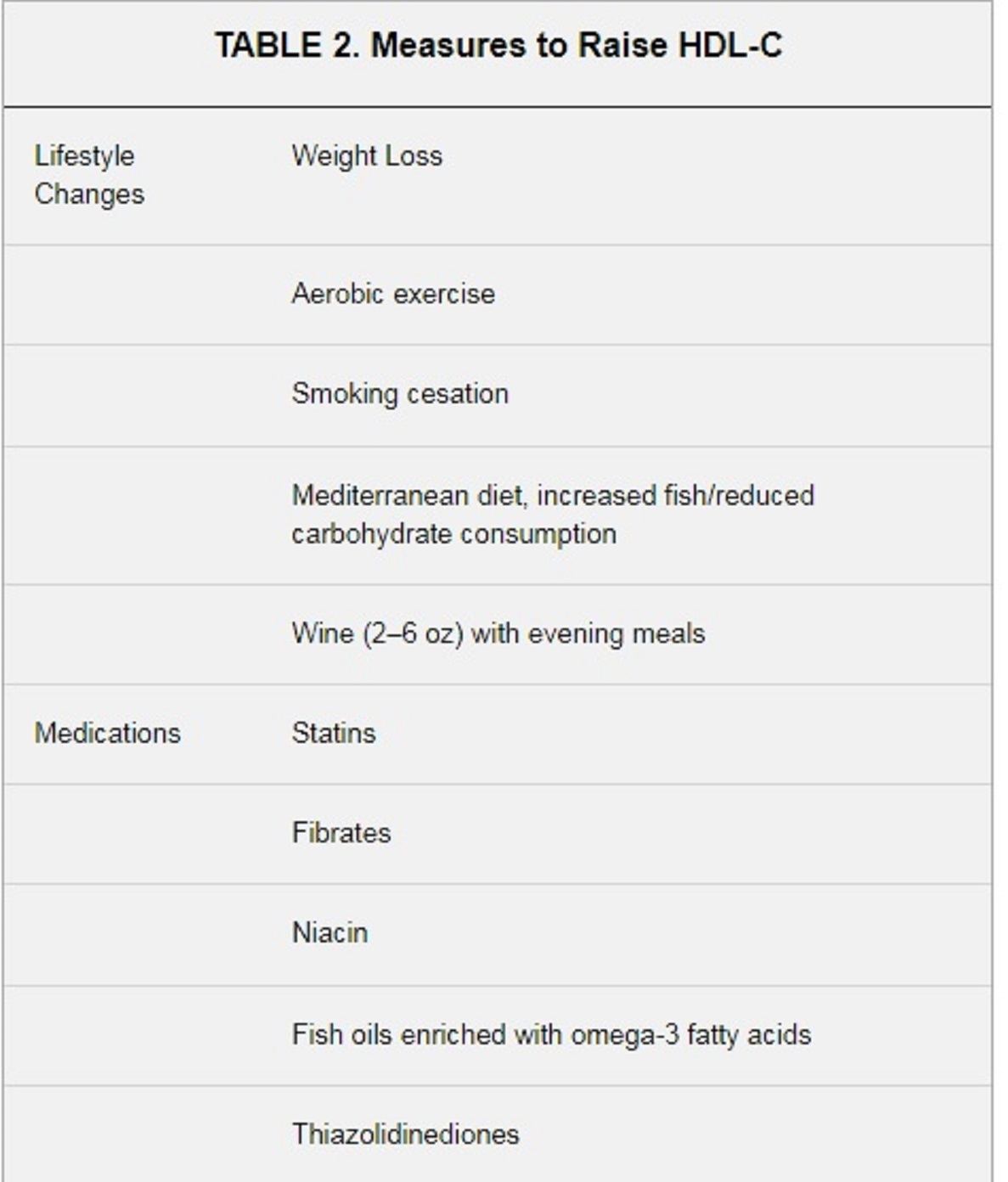
- Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and not smoking can help raise HDL levels.
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein):
- Consider LDL as a “bad cholesterol” from the liver to other areas of our bodies. Elevated LDL levels can result in cholesterol buildup on artery walls.
- The accumulation of plaque can lead to narrowed arteries raising the chances of heart disease and stroke.
- Improving heart health includes reducing LDL levels which can be achieved through lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and regular exercise. For both men and women, normal LDL cholesterol levels should be under 100mg/dL. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to control LDL cholesterol.
Diet and Nutrition Tips to Boost HDL Levels
Here are some diet and nutrition tips to naturally increase HDL levels:
- Choose Healthy Fats: Replace saturated and trans fats with healthier unsaturated fats. Choose to cook using canola, avocado and olive oils. Consume foods like avocados, almonds, seeds and fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel) to add healthy fats to your diet.
- Increase Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Research has shown that omega-3 fatty acids can raise HDL levels. Add fatty fish, chia seeds, flax seeds, and walnuts to your meals.
- Consume Soluble Fiber: Foods rich in soluble fiber can help increase HDL levels. Incorporate oats, barley, beans, lentils, fruits, and vegetables into your diet.
- Eat Fruits and Vegetables: Consume an abundance of colorful fruits and vegetables since they are packed with phytochemicals and antioxidants that are good for your heart.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Moderate alcohol intake, especially red wine, has been associated with higher HDL levels. Moderate alcohol consumption may have health benefits but excessive drinking can be harmful.
- Consider Niacin-Rich Foods: The B3 vitamin niacin is known for raising HDL levels. Poultry, fish, lean meats, whole grains and legumes are foods high in niacin.
- Consume Dark Chocolate in Moderation: Dark chocolate with a high cocoa content contains antioxidants that may have a positive impact on HDL levels. Enjoy it in moderation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water is essential for overall health and may support cardiovascular function.
- Limit Refined Carbohydrates and Sugars: Reduce the intake of processed and sugary foods as they can negatively affect cholesterol levels.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in aerobic activities like brisk walking, running, swimming, or cycling, as regular exercise can improve HDL levels.
- Avoid Smoking: Refrain from smoking as it can reduce HDL levels and raise the risk of heart disease.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight, if needed, can help improve HDL levels and overall heart health.
The Role of Exercise in Improving HDL Cholesterol
Let’s go into more detail about the advantages of exercise for heart health and how it raises HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels:
- Your Body Makes More Good Cholesterol: Regular physical activity such as walking, playing sports, or exercising at the gym prompts your body to produce more “good exercise” known as HDL. This is like having extra cleaners for your blood vessels, helping keep them clear and healthy.
- Cholesterol Cleanup: HDL (high-density lipoprotein) travels through your bloodstream and collects “bad cholesterol” (LDL), which can adhere to your arteries and lead to blockages. HDL cholesterol takes the bad cholesterol back to your liver, where it is removed from your body lowering the risk of heart problems.
- Exercise Helps Break Down Fats: Through exercise, your body becomes better at breaking down fats present in your bloodstream. HDL, with its cleaning powers, works better when there’s less bad cholesterol to pick up. So, exercise helps HDL do its job even better.
- Exercise Helps You Lose Weight: Exercise is beneficial when trying to lose weight as regular physical activity leading to weight loss can raise HDL levels. It’s like getting a bonus boost for your heart health!
- Aerobic or Weight Lifting, Both Work: You don’t have to be a fitness expert to experience the advantages. Participating in different activities like running, biking, swimming or weightlifting can all help increase HDL levels. Find an exercise you like, and it will still benefit your heart.
- Moderate Exercise is good: You don’t need to be a marathon runner or spend hours at the gym to see benefits. Even moderate exercises like brisk walking or dancing can raise HDL levels and support a healthy heart.
- Consistency is Key: Just like with any good habit being consistent with exercise is essential. Consistent exercise boosts HDL levels benefitting your heart health over time.
Remember that maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle entails more than physical activity. Eating a balanced diet, not smoking, and managing stress are also important factors. It’s best to consult your doctor or a fitness specialist if you have any worries about beginning an exercise program or any other aspect of your health. Healthcare professionals can provide guidance and create a personalized plan to meet your needs helping you take better care of your heart.
Factors Affecting HDL Levels
Different factors can have an impact on HDL levels some of which can be adjusted and others of which cannot. Understanding these factors can help individuals make lifestyle changes and take appropriate measures to improve HDL levels and overall cardiovascular health. Here are some of the key factors that can affect HDL levels:
- Genetics: An individual’s HDL levels are strong and it is influenced by their genetics. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to naturally higher or lower HDL levels which can be passed down through family members.
- Hormones: HDL levels can be affected by hormonal changes like those experienced during menopause in women.
- Medications: Some medications including statins used to reduce LDL cholesterol can also influence HDL levels. It’s essential to work with a healthcare provider to monitor and manage cholesterol levels appropriately if taking medication.
- Diseases and Conditions: HDL levels can be impacted by illnesses such as type 2 diabetes, renal disease and liver disease.
- Age and Gender: Women often have higher HDL levels than men. HDL cholesterol levels may decrease with age, but lifestyle modifications can still positively influence them.
- Other Lifestyle Factors: Stress, poor sleep patterns, and lack of physical activity can also affect HDL levels indirectly.
The Importance of the HDL-LDL Ratio
The HDL-LDL ratio is a useful way to assess your heart health. HDL is like the “good cholesterol” that cleans up extra cholesterol from your blood vessels and keeps your heart healthy. LDL on the other hand is sometimes referred to as “bad cholesterol” since it can clog arteries and raise the risk of heart problems.
The ratio shows how much good cholesterol you have compared to bad cholesterol. A higher ratio indicates a greater amount of good cholesterol compared to bad cholesterol which is beneficial for heart health. It suggests a lower risk of heart issues.
Doctors use this ratio to check your heart health and decide if any changes are needed. If your ratio is not ideal, they may recommend lifestyle changes like eating healthier foods, exercising, or sometimes taking medications to improve it.
Remember that the ratio is just one part of understanding your heart health. Other factors like blood pressure, family history, and overall lifestyle also play a role. Therefore, maintaining your heart health by going to the doctor frequently and choosing healthy options is crucial for a strong and happy heart.
HDL Diagnostics: Assessing Heart Health
HDL diagnostics involve tests and evaluations used to measure and assess High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels in the bloodstream. These diagnostic procedures are necessary to evaluate a person’s cardiovascular risk profile and establish whether or not their HDL levels are within a healthy range.
- Lipid Profile Test: The blood test assesses different lipid components such as HDL cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides. The results help healthcare professionals evaluate an individual’s lipid profile and assess their risk of cardiovascular disease.
- HDL Cholesterol Test: Also known as the “good cholesterol” test, this specific test focuses solely on HDL cholesterol levels. It provides information about HDL levels and helps in the evaluation of heart disease risk.
- NMR Lipoprofile Test: This advanced test analyzes the size and number of lipoprotein particles including HDL particles. It can provide more detailed information about lipid sub-fractions.
Ways to Boost HDL Cholesterol and Their Risks
- Niacin (Nicotinic Acid): This medication can increase your HDL levels and simultaneously decrease the levels of LDL (“bad cholesterol”) and triglycerides. Side effects may include flushing (redness and warmth in the skin), itching, and stomach issues. In some cases, it could affect your liver and blood sugar.
- Fibrates (Gemfibrozil, Fenofibrate): Fibrates mainly work on lowering triglyceride levels, but they can also slightly raise HDL levels. Potential side effects could involve digestive issues, muscle discomfort, and rarely liver problems.
- CETP Inhibitors: These are newer drugs that can significantly raise HDL levels by blocking a specific protein involved in cholesterol transfer. Some CETP inhibitors tested have shown concerns about their effects on heart health. Additionally, research is necessary to comprehend their long-term safety.
- HDL Infusions: This therapy involves injecting purified HDL particles into the body to raise HDL levels. The research is in its initial phases and the availability is limited. The safety and effectiveness of this approach need further study.
- Gene Therapy and Novel Approaches: Scientists are exploring new methods, like gene therapy, to raise HDL levels. However, these are still experimental and not used in regular treatments yet. Their potential risks and long-term safety are not fully understood.
Importance of Regular Checkups and Screenings
Monitoring HDL (High-density Lipoprotein) cholesterol levels and general heart health requires routine medical exams and screenings. Here’s why they are crucial:
- Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk: Regular check-ups help assess your overall cardiovascular risk. Evaluating HDL levels, along with other risk factors like blood pressure and LDL cholesterol, provides a comprehensive view of your heart health.
- Personalized Recommendations: Healthcare providers can provide personalized recommendations based on your HDL levels and individual health status. This might include dietary advice, exercise recommendations, and, if needed, medications to improve HDL cholesterol.
- Education and Lifestyle Guidance: During check-ups, healthcare professionals can provide valuable information about the importance of HDL and how to maintain healthy levels. They can offer guidance on heart-healthy habits, like a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
- Monitoring Medication Effects: For individuals on cholesterol-lowering medications, regular check-ups help monitor the medication’s effectiveness and any potential side effects.
Current Research on HDL
Scientists have been researching various aspects of HDL (the “good cholesterol”) to comprehend its potential in enhancing heart health.
- HDL’s Many Roles: HDL isn’t just about moving cholesterol around. Scientists are discovering that it has other jobs too, like being an antioxidant and protecting blood vessels. They’re also investigating the different types of HDL to see how each one helps keep the heart healthy.
- HDL-Like Drugs: Because HDL is protective, scientists are trying to create medicines that work like HDL to boost its benefits. These medications can assist in lowering bad cholesterol and reducing inflammation.
- Clearing Artery Buildup: Researchers are looking into whether increasing HDL levels or improving its function can help remove plaque from artery walls. This could potentially reverse artery buildup and lower the risk of heart problems.
- Studying Genes: Genetic studies have given us useful information about how HDL affects heart risk. By understanding how genes influence HDL, scientists are finding new targets for treatments.
- HDL and the Immune System: HDL can also interact with our immune system and affect inflammation in the body. This might have implications for diseases like atherosclerosis.
- Gut Connection: Some studies suggest that our gut bacteria might influence how HDL works. Researchers are investigating how HDL and gut bacteria might work together to impact heart health.
- Personalized Treatments: With personalized medicine on the rise, researchers are looking at ways to create HDL-based treatments tailored to each person’s unique HDL profile and genes.
- New Ways to Predict Risk: Scientists are exploring new markers related to HDL that could help predict heart disease risk better than traditional cholesterol measurements.
- Lifestyle and HDL: Scientists are continuously studying how lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise can impact HDL levels and function. They’re figuring out which lifestyle changes can best support a healthy heart.
Some Common Questions on High-Density Lipoprotein
What is the ideal HDL-LDL cholesterol ratio for heart health?
The ideal HDL-LDL cholesterol ratio varies based on individual risk factors and health conditions. Higher HDL levels and lower LDL levels are generally preferable. A good HDL total cholesterol ratio is above 24 % and a recommended LDL to HDL ratio is below 3.5.
How often should I get my cholesterol levels checked?
The frequency of cholesterol testing depends on individual risk factors and health status.
In general, adults above 20 years of age should get their cholesterol levels tested every 4-6 years. However, individuals with elevated risk or specific health conditions may require more frequent testing.
Are there specific foods that can boost HDL cholesterol levels?
HDL cholesterol levels can be increased by eating foods high in omega-3 fatty acids such as fatty fish, canola oil and flax seed oil. In addition, soluble fiber-rich meals including oats, beans and fruits help raise HDL levels.
Is HDL cholesterol the only factor that affects heart health?
Heart health is affected by factors like cholesterol levels, blood pressure, physical activity, diet, smoking, family history, and lifestyle changes.
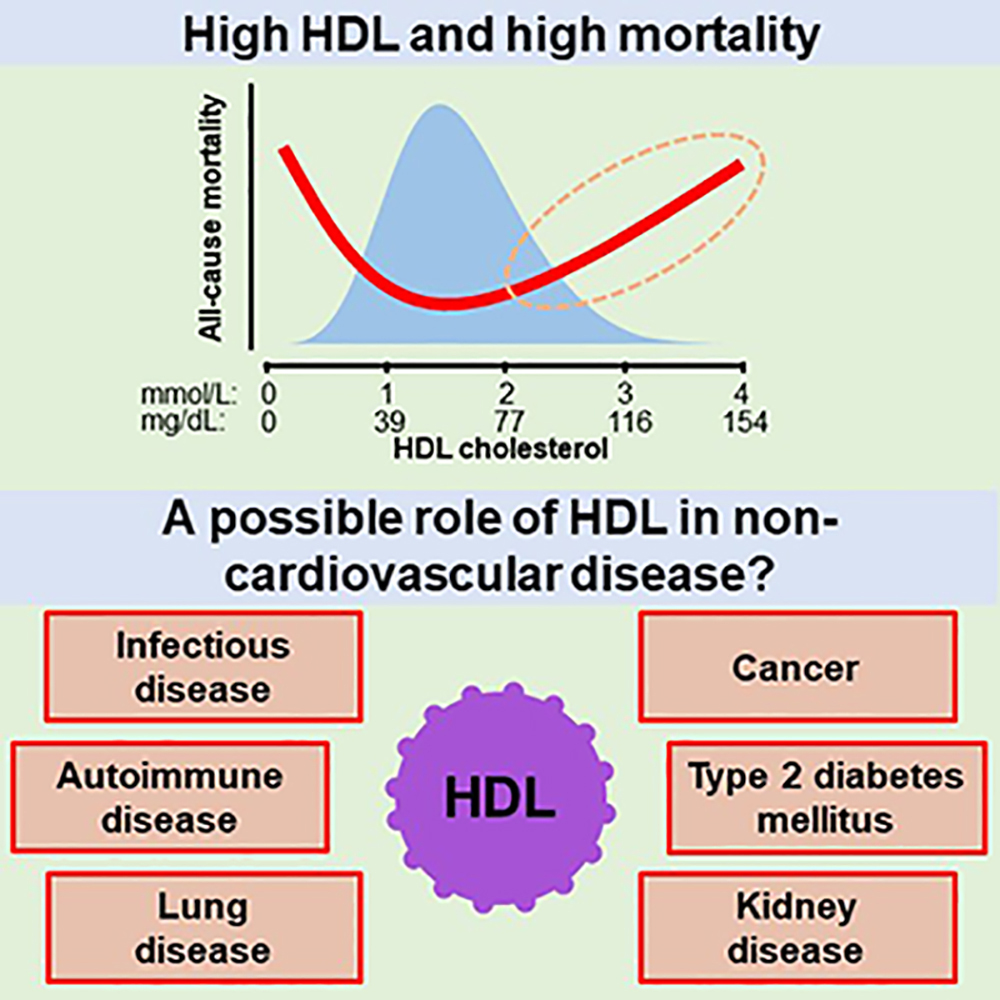
Can HDL cholesterol levels be too high?
While higher HDL levels are generally beneficial for health, excessively high levels may not provide extra advantages or additional protection against heart disease.
Where can I find online support groups for HDL and cardiovascular diseases?
Online platforms such as the American Heart Association’s Support Network, Women Heart, Mended Hearts, and Smart Patients host online communities where you can find support groups specifically related to heart health and HDL cholesterol.









