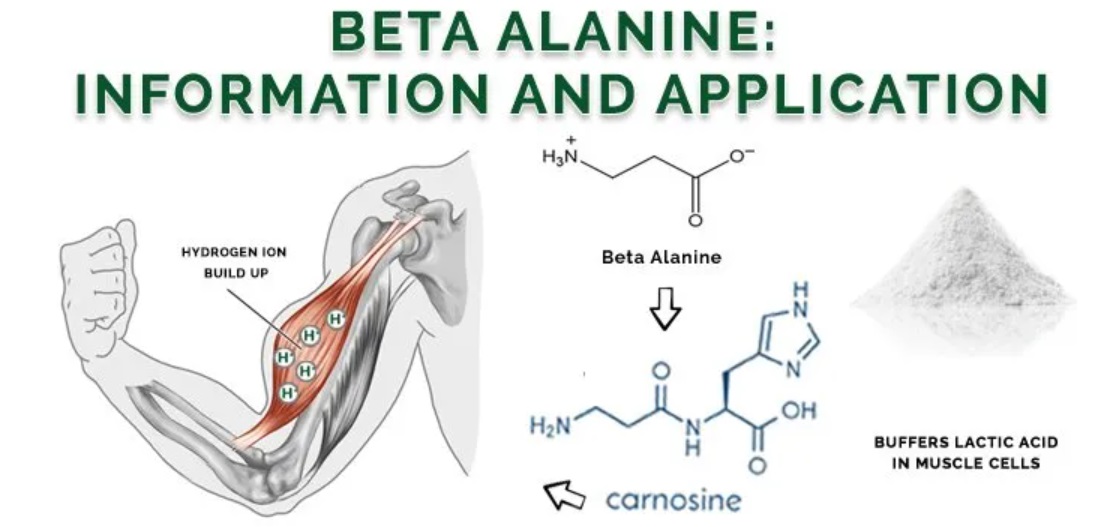
Beta-alanine is a naturally occurring amino acid that is commonly used as a dietary supplement. Beta – alanine is type of amino acid that our bodies can make naturally. Beta –alanine can increase carnosine levels in muscles, which may affect muscle size and performance.

Beta-alanine is generally used by athletes to enhance athletic performance and by elderly individuals to improve physical function. It is occasionally utilized for symptoms associated with menopause, age-related muscle loss, and other health condition. However, the scientific evidence substantiating these applications remains limited in scope.

Natural Food Sources Of Beta-Alanine
Natural food sources of beta-alanine include:
- Meat: Particularly, poultry (chicken, turkey), beef, and pork.
- Fish: Salmon and tuna are known to contain beta-alanine.
- Dairy Products: Milk and cheese are sources of beta-alanine, although in smaller amounts compared to meat and fish.
These food sources provide beta-alanine as part of the overall protein content. It is also found as a dietary supplement to achieve higher levels for specific purposes, such as enhancing athletic performance.
Impact On Various Factors
- Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Exercise maximizes oxygen consumption and metabolic activity that results in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).ROS is generated due to heightened oxygen utilization and metabolic processes during physical activity. If the body’s antioxidant defense mechanisms cannot neutralize these ROS effectively, oxidative stress occurs. This may lead to inflammation, muscle damage, and impaired recovery. Carnosine, formed from beta-alanine and histidine, has shown antioxidant properties in cellular and animal studies. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E are more extensively studied for combating oxidative stress. To address exercise-induced oxidative stress, one should focus on a balanced diet rich in antioxidants.
- Aerobic capacity: Aerobic capacity, also called cardio respiratory fitness, is influenced by factors like cardiovascular fitness, lung function, and the body’s efficient utilization and transportation of oxygen during aerobic exercise. These major factors help in determining an individual’s aerobic capacity, which reflects their ability to maintain prolonged physical activity and endurance. Beta-alanine supplementation helps buffer acid build-up and delay fatigue during high-intensity exercise by increasing muscle carnosine levels.
- Interactions with medications: While beta-alanine generally does not interact with most medications, it is important to exercise caution in certain circumstances. If you have kidney disease or are taking medications that affect kidney function, it is important to consult your healthcare provider before using beta – alanine.
- Weight loss or body composition changes: While beta-alanine can support improved exercise performance and muscle endurance, it does not have a direct impact on fat loss or body composition changes. To achieve weight loss or changes in body composition, it’s important to take a well – rounded approach that includes various factors. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity and potentially creating a calorie deficit.
- Training adaptations: Beta-alanine supplementation has shown to enhance training adaptations by improving muscle endurance and delaying fatigue. It allows individuals to sustain higher training volumes and intensities, leading to greater training adaptations over time. This can lead to enhancements in strength, power and overall athletic performance.
- Intermittent exercise: It consists of repeated bouts of high-intensity activity with brief rest periods. This is especially advantageous for sports and activities involving repeated bursts of intense efforts, such as team sports, interval training, and conditioning workouts.
- Increased training volume: Training volume is related to the total amount of work carried out throughout a training session or over some time. By enhancing muscle buffering capacity and delaying fatigue, beta-alanine allows individuals to tolerate and sustain higher training volumes, leading to potential improvements in endurance and overall training adaptations.
- Training intensity: Training intensity is called a level of effort exerted during exercise measured as a percentage of an individual’s maximum capacity. It enables individuals to maintain higher intensities for longer durations leading to more intense training sessions and potentially greater gains in strength, power, and overall performance.
How Does Beta-Alanine Compare To Other Performance-Enhancing Supplements?
Beta-alanine stands apart from other commonly used performance-enhancing supplements due to its unique mechanisms of action and effects. Here are some examples of other supplements in comparison to B-Alanine;
- Creatine: Creatine primarily enhances strength and power output by increasing ATP production. Beta-alanine, on the other hand, improves muscle endurance and delays fatigue through increased muscle carnosine levels.
- Caffeine: Caffeine is a stimulant that can increase energy levels and focus, making physical activity feel easier.
- BCAAs: BCAAs support muscle recovery and reduce muscle breakdown, but they do not have the same buffering effects on muscle pH and performance enhancement as beta-alanine.
- Nitric Oxide Boosters: Nitric oxide boosters enhance blood flow, vasodilation and the transportation of nutrients to the muscles. Beta-alanine does not directly impact blood flow but focuses on enhancing muscle buffering capacity and endurance.
While these supplements can work together synergistically, it is crucial to comprehend their individual impacts and the underlying mechanisms by which they operate.
The Effects Of Beta-Alanine On High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) Performance
Taking beta –alanine as a supplement has been shown to have positive effects on both high – intensity interval training (HIIT) performance and recovery.
Here are the key points to consider:
- Performance Improvement: Beta-alanine can enhance performance during HIIT by delaying fatigue and improving muscle endurance. This can allow individuals to sustain higher intensities for longer durations during intense intervals of HIIT workouts.
- Acid Buffering: HIIT often leads to the accumulation of lactic acid, causing muscle acidosis and fatigue. Beta-alanine increases muscle carnosine levels, which act as buffers and help regulate pH levels. This buffering effect can be advantageous during HIIT sessions with repeated intense exercises.
- Recovery Enhancement: HIIT places substantial stress on the body, and proper recovery is crucial for optimal performance and adaptation. Taking beta – alanine as a supplement after a workout may help with recovery by reducing muscle damage and oxidative stress. This can potentially result in faster recovery between HIIT sessions and improved overall training adaptations.
- Individual Variability: The response to beta-alanine supplementation can vary among individuals. Factors such as baseline carnosine levels, training status, and individual metabolism can influence the extent of improvement in HIIT performance and recovery.
The Potential Benefits Of Β-Alanine Supplementation
Research has indicated that β-alanine supplementation can be favorable for human health and performance. It is believed to increase muscle carnosine levels which can potentially enhance exercise performance. Beta-alanine may contribute to the growth and maintenance of lean muscle mass, particularly when fused with proper training and nutrition. Some of the other benefits are;
- Concentration: Beta-alanine supplementation may enhance cognitive function and concentration by reducing mental fatigue and improving focus, possibly through increased muscle carnosine levels.
- Energy Production during Fasting: β-Alanine serves as a source of energy during fasting periods, preventing muscle breakdown and supporting glucose conversion in the liver.
- Prostate Health Support: β-Alanine is found in high concentrations in prostate fluid and may help protect the prostate gland, reducing symptoms associated with prostate problems and providing antioxidant benefits.
- Psychiatric Conditions: Clinical trials exploring carnosine or beta-alanine supplementation have reported promising results in various psychiatric disorders, including autism spectrum disorders. For instance, studies have shown that carnosine supplementation can reduce negative symptoms of schizophrenia and improve executive functions in patients receiving treatment.

- Glycemic Control in Individuals with Diabetes: Beta-alanine supplementation improved glycemic control in individuals with diabetes by reducing fasting blood sugar levels. It’s important to note that beta–alanine supplementation does not directly affect glucose metabolism or regulation.
- Exhaustion: Beta-alanine supplementation delays muscle fatigue and exhaustion, improving exercise performance.
- Resistance training: It maximizes resistance training performance by enhancing strength, power, and endurance.
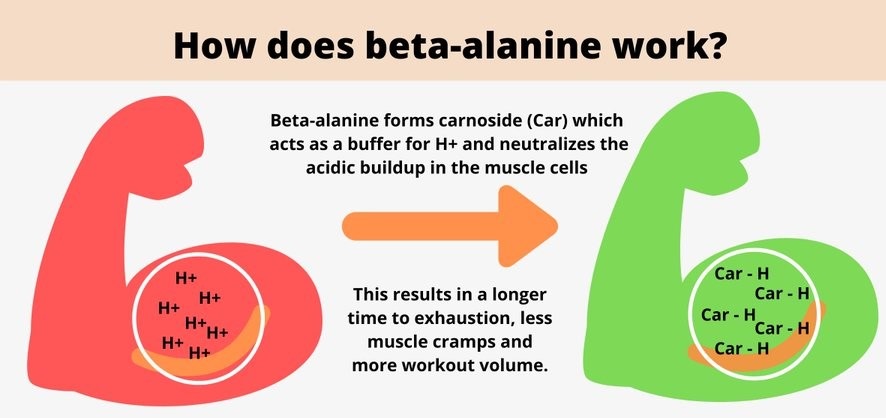
- Glycolysis: In high-intensity exercise, glycolysis is a key metabolic pathway that provides energy. Beta-alanine supplementation has found to raise muscle carnosine levels, which aids in buffering the buildup of hydrogen ions. This buffering effect delays muscle fatigue during glycolytic activity, enabling individuals to sustain intense exercise for longer durations.
Side Effects Of B-Alanine
- Paresthesia: Temporary tingling or flushing sensation called paresthesia can occur as mild side effects with beta-alanine supplementation.
- Gastrointestinal Distress: Mild gastrointestinal issues like stomach discomfort, nausea, or diarrhea is also possible among some people.
- Allergic Reactions: In unusual cases, individuals can have allergic reactions such as itching, rash, or swelling. Discontinue the use of beta-alanine and seek medical attention if any allergic conditions occur.
The Function Of Beta-Alanine Supplementation And Muscle Carnosine Content
Beta-alanine supplementation increases muscle carnosine content, benefiting exercise performance and muscle function. Muscle carnosine content ranges from 15 to 40 mmol/kg of dry muscle weight, influenced by age, sex, fitness, and diet. Higher carnosine levels support optimal muscle function and performance.
The Role of Beta-Alanine in Carnosine Synthesis and Muscle Performance
Beta-alanine serves as a building block for the synthesis of carnosine. When beta-alanine is consumed or supplemented, it is taken up by muscle cells and combined with histidine to form carnosine. This process is facilitated by an enzyme called carnosine synthase.
Carnosine is predominantly found in skeletal muscle tissue, particularly in fast-twitch muscle fibers. It plays several important roles in muscle function and performance. One of its primary functions is acting as a buffer to regulate pH levels within the muscle during intense exercise.

In high-intensity activities like weightlifting or sprinting, the breakdown of glucose leads to the production of lactic acid for energy production. Lactic acid accumulation can cause a decrease in pH, resulting in muscle fatigue and reduced performance. However, carnosine acts as a pH buffer and helps maintain a more neutral pH environment within the muscle.
By increasing muscle carnosine levels through beta-alanine supplementation, individuals may experience improved buffering capacity, delaying the onset of muscle fatigue and allowing for greater exercise intensity and duration. This can potentially lead to enhanced athletic performance, increased strength, and improved muscle endurance.
FAQs on Beta- Alanine:
Is Beta-Alanine found in pre-workout supplements?
Beta-alanine is generally found in pre-workout supplements. They are formulated to enhance performance, energy, and focus during exercise. Beta-alanine is offered in different forms to accommodate individual preferences and requirements. It includes pure beta-alanine powder or capsules, blends with additional ingredients such as creatine or caffeine, and pre-workout or intra-workout formulas designed to boost exercise performance and endurance. These varied formulations provide options for selecting the most suitable choice based on personal goals and preferences.
How soon one can expect to see results from Beta-alanine supplementation?
When taking beta-alanine as a dietary supplement, it typically takes several weeks of consistent daily supplementation to notice results. Some people may start to notice improvements in endurance, power output, and fatigue resistance within a few weeks, while others may require a longer time of supplementation to experience noticeable effects.
Studies have shown that people taking regular supplementation with recommended dosages can notice muscle carnosine levels increase by approximately 40-80% after 4 to 6 weeks (usually ranging from 4 to 6 grams per day).
What is the recommended dosage of Beta-Alanine?
The recommended dosage of beta-alanine can differ based on individual factors like body weight, tolerance, and goals. A typical recommendation is to take 4 to 6 grams of beta –alanine per day, divided into several smaller doses. For maximum benefits, it is recommended to divide the daily beta-alanine dosage into 2 to 4 smaller doses taken throughout the day.
Is Beta-Alanine safe for long-term use?
Beta-alanine is generally regarded safe for extended periods of supplementation when consumed within the recommended dosage guidelines.
Can It enhance performance in team sports?
Beta-alanine supplementation is more beneficial for team sports that involve frequent high-intensity actions, quick changes of direction, and short recovery periods, compared to sports with longer periods of low-intensity activity.
It allows athletes to sustain higher levels of performance for longer duration and benefits team sports where games can last for extended periods. Activities such as sprinting, jumping, changing direction, and tackling can benefit from beta-alanine’s ability to improve performance during intense bursts of energy. By increasing the muscle’s buffering capacity, beta-alanine helps maintain optimal pH levels and delays fatigue in the anaerobic energy system commonly used in team sports.
How It works in muscle fiber?
The response to beta-alanine supplementation can be influenced by muscle fiber type. Slow-twitch fibers primarily rely on aerobic metabolism, while fast-twitch fibers mainly depend on anaerobic metabolism and are more susceptible to fatigue. Beta-alanine primarily enhances the buffering capacity of fast-twitch muscle fibers due to their higher carnosine levels. This can benefit activities requiring high-intensity, anaerobic efforts. It’s important to understand that the impact of beta –alanine on the muscle fatigue thresh hold can vary from person to person.
Exploring the types and considerations of Beta-Alanine Supplements
Beta-alanine supplements come in various forms, including pure beta-alanine, blends with other ingredients like creatine or caffeine, pre-workout formulas, and intra-workout formulas. It is crucial to read product labels, follow recommended dosages, and seek professional advice before incorporating any beta-alanine supplementation into your routine.
Can we take protein and B-Alanine together?
Yes, it is possible to take protein and beta-alanine supplements together. Many athletes and individuals were interested in maximizing their performance and muscle development and often combine protein supplements with beta-alanine supplementation. Protein provides the necessary amino acids for muscle growth and repair, while beta-alanine helps enhance exercise performance and delay muscle fatigue.









