Omega-6 fatty acids are fascinating substances that have drawn the interest of health enthusiasts and researchers due to their significant effects on our overall health. Did you know that omega-6 fatty acids are considered essential fats? This means, our bodies cannot produce them naturally, so we must obtain them from our diet.
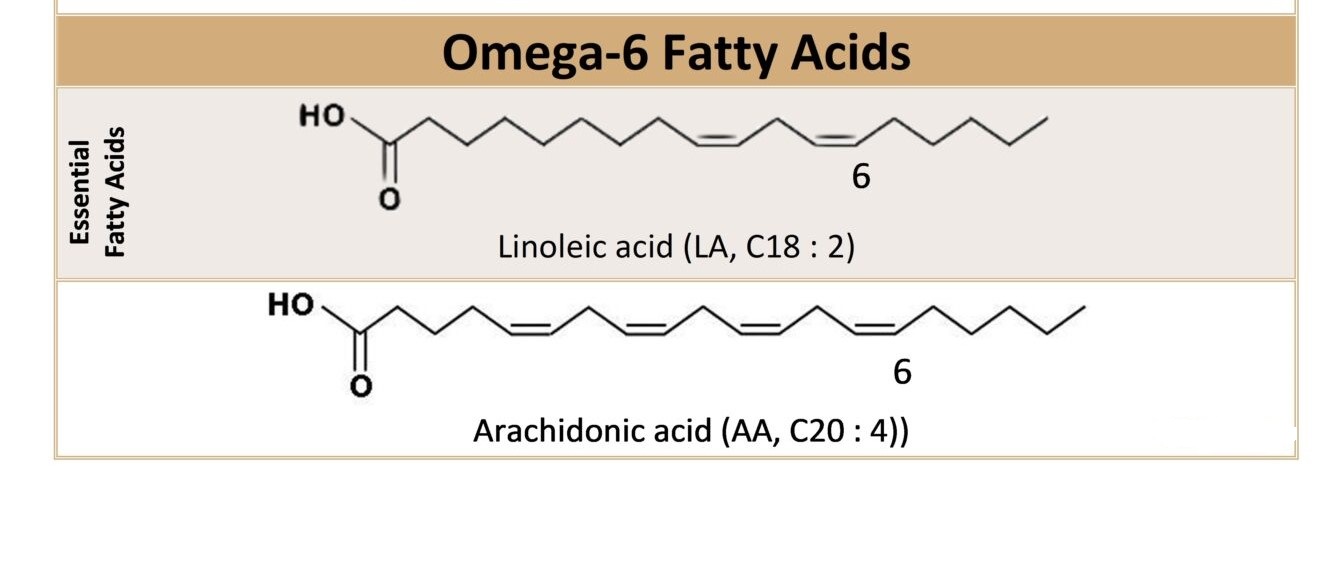
Data indicates that omega-6 fatty acids are extensively consumed in modern diets, mainly through processed and refined oils. Omega-6 fatty acids have been associated with various health benefits. Studies suggest that omega-6 fatty acids can be good for our heart, brain, skin and hair. This might lower the risk of heart issues, support brain health and improve the appearance of our skin and hair. Including these fatty acids in our diet could be beneficial for our overall health. By understanding their role and incorporating them into our diet, we can unleash their full potential.
Types of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
- Linoleic Acid (LA): This particular omega-6 fatty acids is abundant in our bodies and is the most prevalent. It falls under the category of essential fatty acids implying that the body cannot produce it and needs to be obtained from the diet.
- Arachidonic Acid (AA): Arachidonic acid is an important substance in our body that comes from another fatty acid called linoleic acid. It acts as a building block to create special messengers that help our body communicate and carry out important tasks. These messengers play a critical role in various processes such as controlling inflammation, supporting brain function and regulating different body functions.
- Gamma-Linoleic Acid (GLA): GLA is an omega-6 fatty acid that isn’t found in many foods, but our body can produce it by converting another fatty acid called linoleic acid.
Health Benefits of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to fight infections and help heal injuries. But prolonged inflammation is not healthy and can cause different disorders.
Omega-6 fatty acids can affect inflammation in our body. They can either increase or decrease inflammation depending on the situation. Omega-6 fatty acids are necessary for a strong immune system and assist our body in healing when consumed in appropriate quantities. However, if we consume too much omega-6 fatty acids, especially from unhealthy sources, it can upset the balance and cause more inflammation. So, it’s crucial to find the right balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. But if the balance is off, it could lead to more inflammation, which might be linked to chronic diseases like heart problems, obesity and certain types of cancer. So, including a variety of healthy foods in our diet and being mindful of our fatty acid intake can keep our body in good shape and reduce the risk of health issues.
Omega-3 fatty acids, which are present in fatty fish, flax seeds and walnuts have anti-inflammatory properties and can help balance out the pro-inflammatory effects of omega-6 fatty acids. To have a healthy diet, it’s essential to control or reduce the intake of processed foods that contain unhealthy omega-6 fatty acids.
It is worth nothing that the effects of omega-6 fatty acids can differ among people. People vary in their sensitivity to the pro-inflammatory effects of omega-6 fatty acids. Individuals differ in how sensitive they are to the effects of fatty acids. Some people may be more susceptible to these effects, while others may not experience any negative consequences. Listening to your body and making dietary choices based on your individual needs and preferences is beneficial.
Role of Omega-6 Fatty Acids in Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Omega-6 fatty acids positively affect brain health and cognitive function. It is essential for maintaining the structure and optimal functioning of our brain cells. Our brain needs different nutrients to work as its best and one of these important nutrients is omega-6 fatty acids. They are involved in creating cell membranes in the brain, which protects and enhances communication between brain cells. Research has indicated that omega-6 fatty acids may have positive effects on cognitive function especially in areas like memory, attention and mood regulation.
Omega-6 fatty acids are crucial for brain health but an excessive amount of them can be harmful. The best approach is to maintain a balanced diet with various nutrients, including omega-6 fatty acids to support optimal brain function.
Omega-6 fatty acids and cardiovascular health
- Cholesterol Levels: Linoleic acid (LA) is an omega-6 fatty acid which has the potential to influence cholesterol levels in the body. Studies have shown that a moderate intake of omega-6 fatty acids specifically those containing linoleic acid (LA) can have a positive effect on cholesterol levels. It helps lower total cholesterol and the “bad” cholesterol called low-density lipoprotein (LDL). A review of studies found that replacing 5% of our energy intake from saturated fatty acids with omega-6 fatty acids resulted in 19 % decrease in the risk of coronary heart disease. The effect on cholesterol levels is influenced by how omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids interact in the diet, as well as other lifestyle factors.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: GLA, an omega-6 fatty acid has the potential to positively regulate blood pressure levels. Some studies suggest that GLA supplementation can help lower blood pressure levels in individuals with hypertension.
Dietary Sources of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
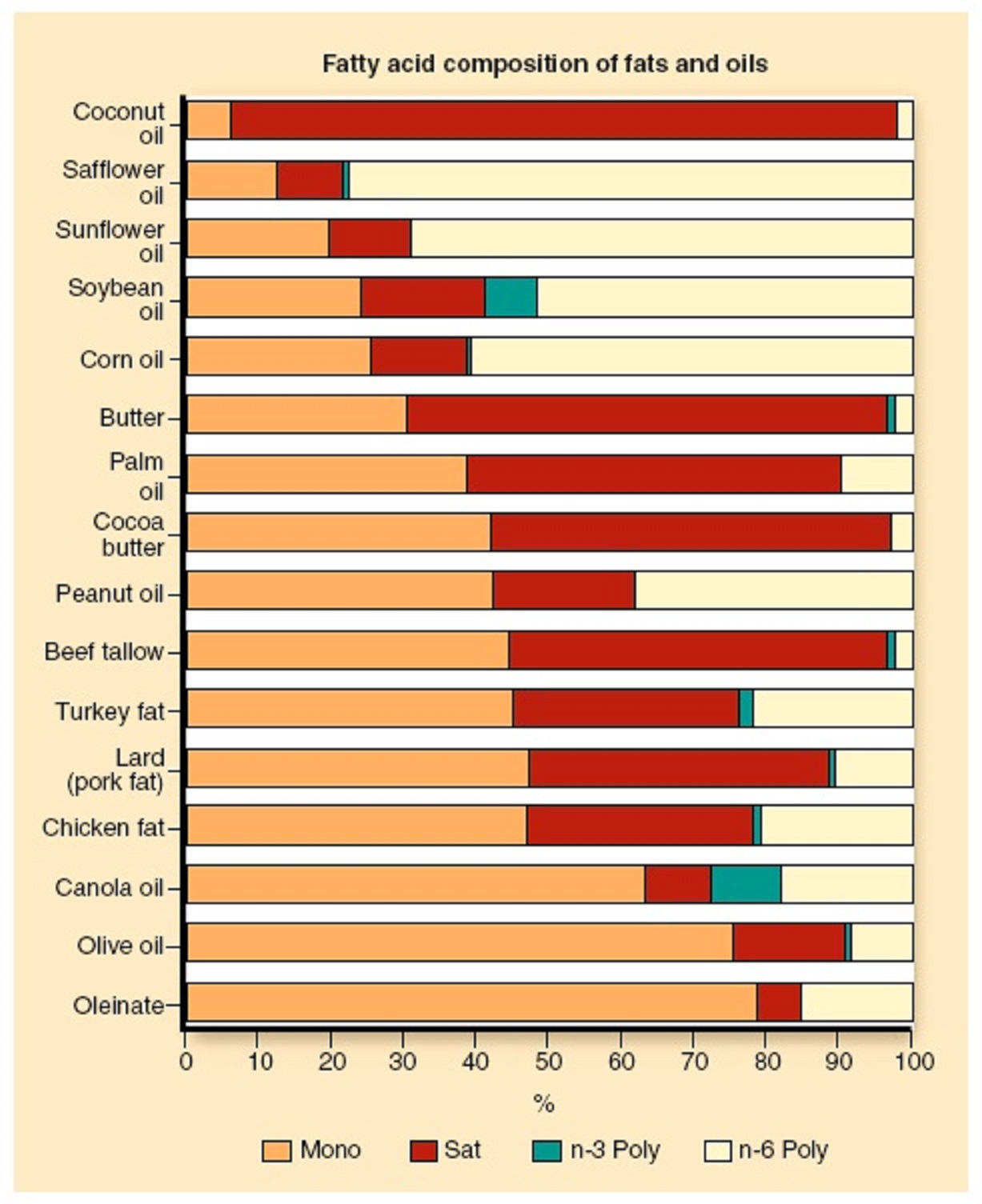
- Vegetable Oils: Statistics indicate that vegetable oils like soya bean oil, corn oil and sunflower oil are commonly consumed and contribute significantly to our intake of omega-6 fatty acids. Indeed, vegetable oils make up a significant part of the calorie intake in various Western diets. The prevalence of vegetable oil usage highlights their importance as a major dietary source of omega-6 fatty acids.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds are full of omega-6 fatty acids, which are important for our body’s health. Walnuts, sunflower seeds and sesame seeds are some examples of these foods. The most common omega-6 fatty acid is called linoleic acid. Including these foods in our diet is like adding essential pieces to our body’s nutritional requirements.
- Meat and Poultry: Meat and poultry products can also be significant sources of omega-6 fatty acids. It’s important to know that the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids in animal-based products can change depending on what the animal eats. Animals that eat grass have a more favorable balance of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids compared to those that consume grain-based diets. Understanding the dietary sources of omega-6 fatty acids in animal products allows for making informed choices that align with one’s nutritional goals.
- Processed and Packaged Foods: Vegetable oils rich in omega- fatty acids are commonly found in processed and packaged foods including cookies, crackers, snack bars and fried snacks. However, it is crucial to moderate the consumption of such foods as they often contain excessive levels of unhealthy fats and additives.
Measuring Omega-6 Fatty Acids
- Blood Tests: Blood tests such as fatty acid profile can offer insights into the concentrations of various fatty acids including omega-6 fatty acids present in the blood.
- Tissue Biopsy: In certain situations, a tissue biopsy may be done to directly measure the levels of omega-6 fatty acids in specific body tissues, like fat or muscle. This helps understand the amount of these fatty acids present in the body.
- Dietary Assessment: Evaluating dietary intake through food diaries or dietary questionnaires can estimate the amount of omega-6 fatty acids consumed. This method provides an indirect measurement of omega-6 fatty acid intake.
- Nutritional Databases: Nutritional databases and software can provide estimates of omega-6 fatty acid content in different foods, allowing for calculations of intake based on food consumption records.
Omega-6 to Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratios: Recommended Intake
- Recommended Daily Intake: There is no specific Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) established for omega-6 fatty acids. Various health organizations suggest that adults should obtain around 5 % to 10 % of their daily intake from omega-6 fatty acids. For an average 2,000-calorie diet, this translates to approximately 11 to 22 grams of omega-6 fatty acids per day.
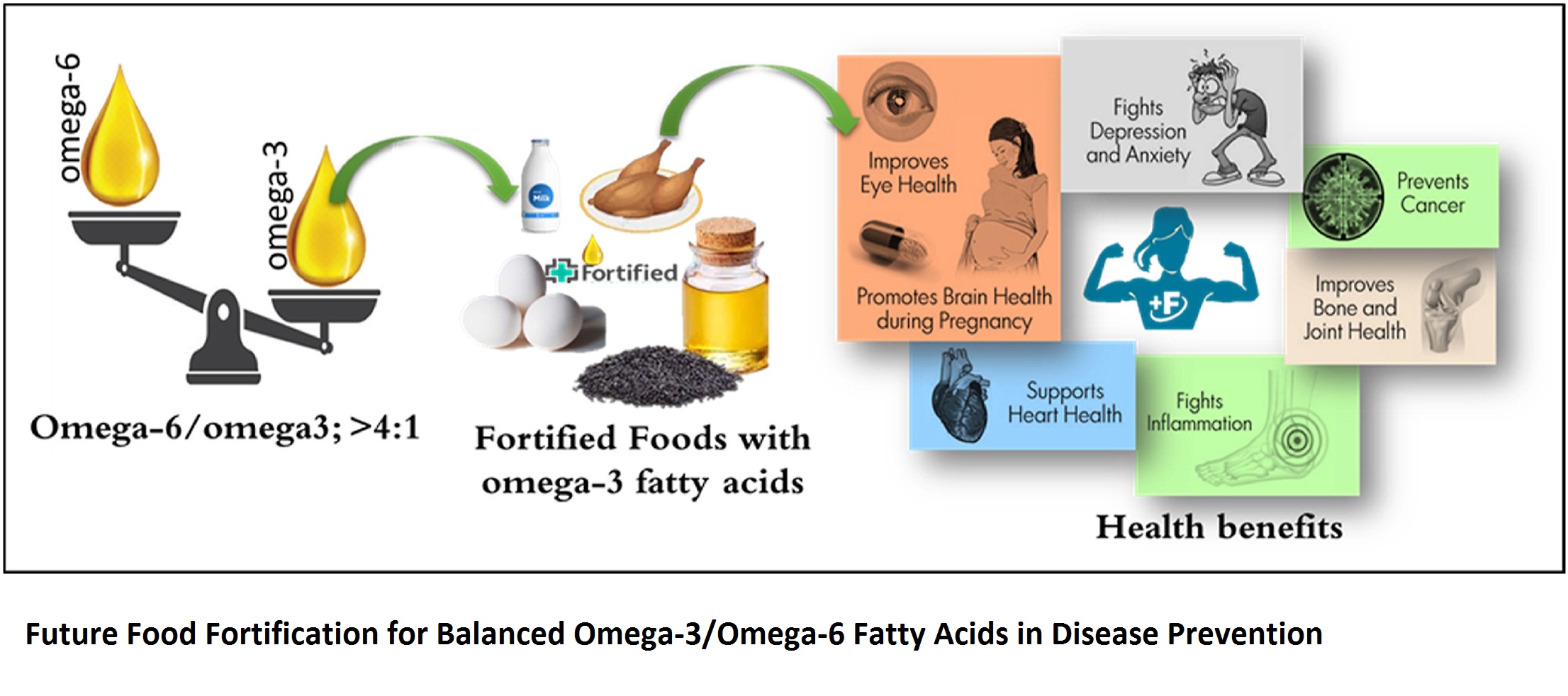
- Omega-6 to Omega-3 Ratio: Maintaining a proper balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acid is crucial. Research suggests that the ideal ratio between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids is around 4:1 or lower. However, the typical Western diet often has a higher ratio, estimated to be around 15:1 or even higher. Achieving a balanced ratio can help to maintain a healthy inflammatory response and support overall health.
In the future, there is a potential for the development of food fortification strategies that include a balanced ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the diet. This fortification approach aims to prevent lifestyle diseases by optimizing the intake of these essential fatty acids in the diet.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids and Skin Health
- Skin Barrier Function: Omega-6 fatty acids are crucial for preserving the integrity and functionality of the skin barrier. They play a role in the creation of lipid bilayers in the outermost layer of the skin, which is known as the stratum corneum. A healthy skin barrier helps protect against environmental irritants and prevent water loss from the skin.
- Hydration and Moisture: Omega-6 fatty acids enhance skin hydration by improving the effectiveness of the skin’s natural moisturizing components. A balanced intake of omega-6 fatty acids can contribute to overall skin hydration.
- Skin Aging: Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress can accelerate skin aging. By keeping a balanced ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids, one can promote a healthy inflammatory response, reduce oxidative damage, potentially slow down the aging process and support skin health.
Omega-6 fatty acids and skin conditions
The relationship between omega-6 fatty acids and conditions like eczema and psoriasis is intricate and not completely understood. Here are some examples of their relationship:
- Eczema: Eczema or atopic dermatitis is a long-term skin problem characterized by dry, itchy and irritated skin. Some studies suggest that an imbalance in omega-3 fatty acids, an excessive intake of omega-6 fatty acids can lead to inflammation and potentially exacerbate symptoms of eczema. However, more research is needed to establish a clear relationship and optimal balance between these fatty acids in managing eczema.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to thick, red, scaly patches on the skin. While the exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, inflammation plays a significant role in its development and progression.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids and Hormonal Balance:
- Reproductive Hormones: Omega-6 fatty acids are involved in the production and regulation of reproductive hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone in females, and testosterone in males. These hormones are crucial for the development of reproductive organs, regulation of menstrual cycles, promotion of fertility and maintenance of overall reproductive well-being.
- Prostaglandin Synthesis: Omega-6 fatty acids help in the regulation of hormone levels. One example is their involvement in the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles in the uterus during menstruation and childbirth. They also participate in the regulation of hormone secretion in various glands throughout the body.
- Inflammation and Menstrual Symptoms: Excessive inflammation can be a contributing factor to menstrual symptoms such as pain, cramps and heavy menstrual bleeding. Achieving a balanced ration of omege-6 to omega-3 fatty acids may assist in reducing inflammation and easing symptoms related to menstruation.
Some Common Questions On Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Can consuming omega-6 fatty acids help with joint health and arthritis?
The effects of consuming omega-6 fatty acids on joint health and arthritis are subject to debate as the evidence presents a mixed perspective. Consuming an excessive amount of omega-6 fatty acids without a proper balance of omega-3 fatty acids can potentially exacerbate arthritis symptoms, despite the anti-inflammatory properties of omega-6 fatty acids. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended for personalized guidance.
Are there any potential risks or side effects of consuming too much omega-6 fatty acids?
Excessive consumption of omega-6 fatty acids without sufficient omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to an imbalance that promotes inflammation and may increase the risk of chronic diseases. High intake of omega-6 fatty acids may elevate LDL cholesterol levels and potentially have negative effects on cardiovascular health.
Are there any interactions between omega-6 fatty acids and medications?
As a general rule, omega-6 fatty acids when consumed as part of a balanced diet do not usually exhibit significant interactions with medications. Omega-6 fatty acids can mildly thin the blood and in large amounts, they may interact with certain medications, like blood thinners (e.g., warfarin), which also have similar effects.
Are omega-6 fatty acids suitable for infants or children?
Omega-6 fatty acids are essential for the growth and development of infants and children playing a critical role in their overall health and well-being. In infancy, omega-6 fatty acids, particularly arachidonic acid (ARA), are vital for the development of the central nervous system and visual system. ARA is naturally found in breast milk and is also added to infant formula to ensure adequate intake. It helps support cognitive function, vision development, and the growth of healthy skin.
Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional or pediatrician is recommended to ascertain the specific nutritional requirements for infants and children.
Can omega-6 fatty acids enhance exercise-induced fat loss?
Some evidence suggests that omega-6 fatty acids may play a small role in enhancing fat loss during exercise. These fats can help our body use stored fat for energy during workouts. However, the overall impact on fat loss is modest and it’s more important to focus on a balanced diet and regular exercise for effective weight management.
What are the common omega-6 fatty acid supplements available?
Some of the most common one include:
- Evening primrose oil: It is rich in gamma-linoleic acid (GLA), a beneficial omega-6 fatty acid.
- Borage oil: Similar to evening primrose oil, borage oil is another source of GLA.
- Black Currant seed oil: This supplement also contains GLA and is derived from black currant seeds.
- Hemp seed oil: Hemp seed oil contains a good balance of both omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Safflower oil: This oil is high in linoleic acid, another essential omega-6 fatty acid
- Sunflower oil: This oil is rich in linoleic acid which is an essential omega-6 fatty acid.









