Having a grasp of the nutritional composition of our food is crucial for sustaining a nutritious and well-rounded diet. Through a thorough examination of various meals, we can reveal their advantages and drawbacks, empowering us to make knowledgeable decisions regarding our dietary preferences. This assessment assists us in gauging the extent to which our meals harmonize with our dietary objectives, whether they pertain to weight control, muscle development, or general health and well-being.
Monitoring Macro Percentages
Maintaining a balanced diet is key to achieving health and fitness goals. Central to this balance is keeping a close eye on your macronutrient (macro) percentages.
Understanding Macronutrients:
- Carbohydrates: The primary energy source for the body. They should make up a significant portion of your daily intake, especially if you engage in regular physical activity.
- Proteins: Essential for muscle repair, growth, and overall health. Adequate protein intake is particularly important for those involved in strength training and exercise.
- Fats: Necessary for various bodily functions, including energy storage and nutrient absorption. Opt for healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, and fatty fish.
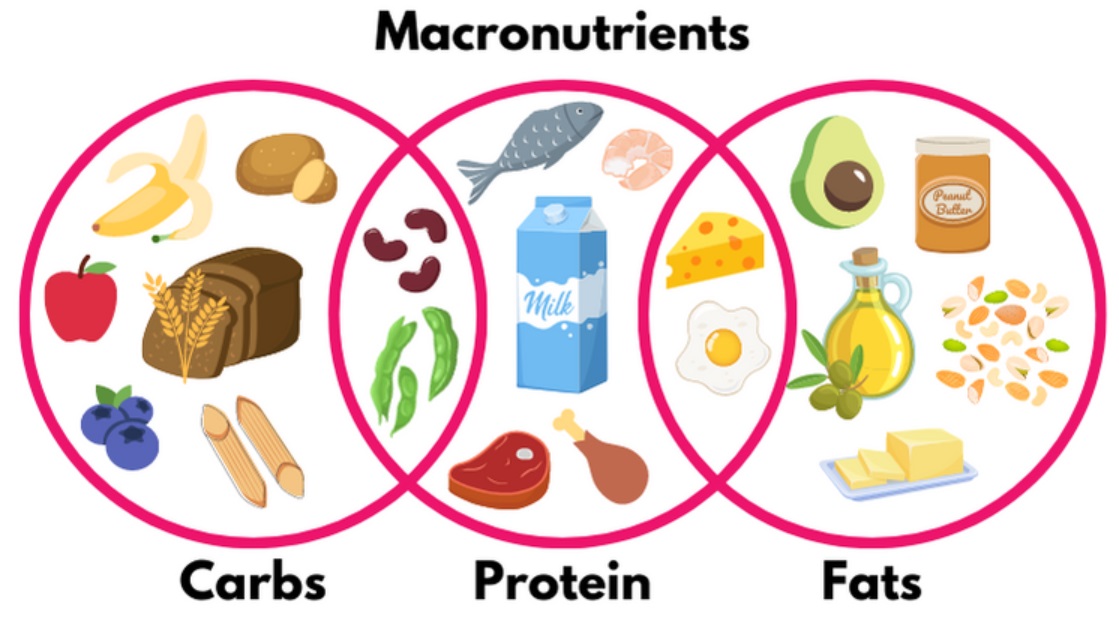
Balanced Intake: A well-balanced diet consists of a specific distribution of macros tailored to your goals. Whether you’re striving for weight loss, muscle gain, or maintaining your current physique, your macro percentages will vary accordingly.
Nutrient Timing: Pay attention to the timing of your macros. Pre-workout, a meal or snack rich in carbohydrates can fuel your exercise. Post-workout protein intake can aid muscle recovery.
Dietary Imbalance: Neglecting macro percentages can lead to dietary imbalances, such as excessive carb consumption that can contribute to weight gain or inadequate protein intake, hindering muscle development. The key is to find the right macro balance that aligns with your objectives.
Individual Variation: Keep in mind that macro needs can vary among individuals due to factors like age, gender, activity level, and metabolism. Customizing your diet to your specific requirements is crucial.
Calculating Your Macro Percentages
To determine the ideal macro percentages for your daily intake, follow these steps:
- Set Your Caloric Intake: Start by determining your daily calorie target based on your fitness goals. Whether you want to maintain, lose, or gain weight, this caloric baseline serves as the foundation for your macro percentages.
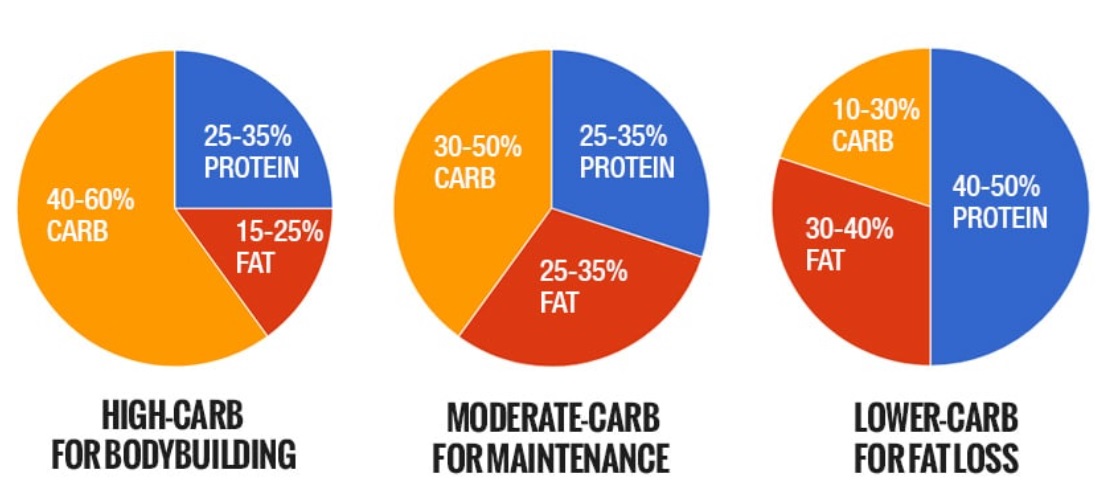
- Establish Protein Intake: Protein is crucial for muscle maintenance and growth. A common recommendation is to allocate 20-30% of your total daily calories to protein. If you’re engaging in intense strength training, you may lean toward the higher end of this range.
- Distribute Carbohydrates: The remaining calories should be divided between carbohydrates and fats. Carbohydrates are essential for energy, especially if you have vigorous workout routines. Allocate about 45-65% of your daily calories to carbohydrates.
- Allocate Healthy Fats: The remaining calories are designated for fats. A suitable range is typically 20-35% of your daily calories. Healthy fats are crucial for hormonal balance and overall well-being.
- Do the Math: Once you’ve set your daily calorie target and established your percentages for each macronutrient, you can calculate the specific grams of protein, carbohydrates, and fats to consume. You can use online calculators or consult with a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
- Monitor and Adjust: After you’ve determined your daily macro percentages, it’s crucial to monitor your progress. Regularly evaluate your performance, energy levels, and body composition to make necessary adjustments to your macronutrient ratios.
The Significance of Protein in a Meal
- Muscle Repair and Growth: Protein serves as the building block of muscles. After a strenuous workout, muscles often experience micro-tears. Protein intake is essential for repairing and rebuilding these muscle tissues. This not only aids in recovery but also promotes muscle growth and strength.

- Improved Exercise Performance: Protein provides the body with the necessary amino acids, which are crucial for endurance and performance during workouts. Adequate protein intake can help maintain energy levels, reduce fatigue, and enhance exercise capacity.
- Satiety and Weight Management: Protein-rich meals tend to create a feeling of fullness and satiety. This can be a valuable asset for individuals striving to manage their weight. Feeling satisfied after a meal can deter overeating and snacking, contributing to weight control.
- Fat Loss: Protein has a high thermic effect, which means it requires more energy to digest compared to fats and carbohydrates. This increased energy expenditure can contribute to fat loss and improved body composition.
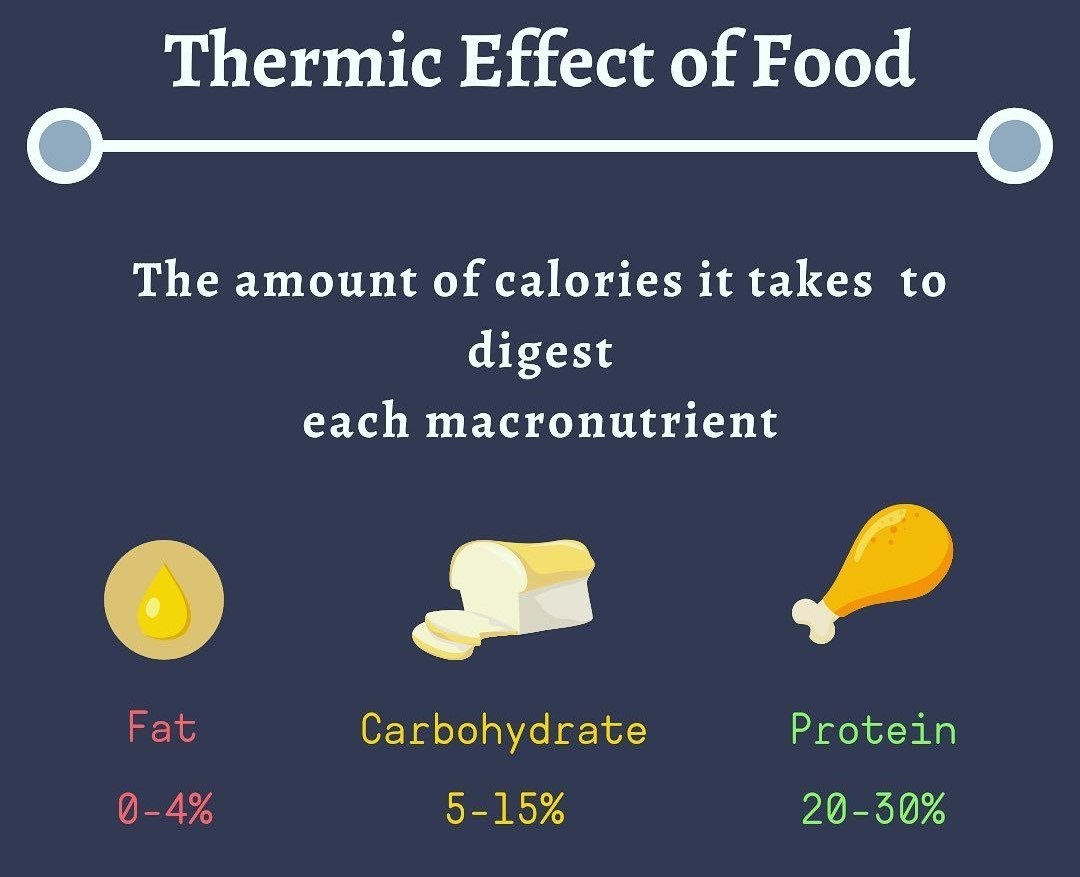
- Enhanced Recovery: Protein consumption post-workout is known to accelerate recovery by reducing muscle soreness and inflammation. This ensures that individuals can return to their workout routines more quickly and with reduced discomfort.
- Nutrient Delivery: Protein can assist in the absorption of essential nutrients like iron and calcium from other foods. This is particularly beneficial for athletes who have higher nutrient requirements due to their active lifestyles.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: It can help stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing drastic spikes and crashes.
Selecting Nutrient-Rich Protein Sources
- Lean Meats: Opt for lean cuts of beef, pork, and poultry. These sources are rich in protein and lower in saturated fats, making them an excellent choice for muscle building.
- Fish: Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and trout provide not only protein but also essential omega-3 fatty acids, which contribute to overall health.

- Dairy: Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and low-fat milk are excellent dairy sources of protein. They also supply calcium for strong bones.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are plant-based protein sources that are high in fiber and other nutrients.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are protein-rich choices that also deliver healthy fats and micronutrients.
Analyzing Nutritional Strengths of Our Meals
- Macronutrient Balance: A meal rich in lean protein sources such as chicken breast, accompanied by complex carbohydrates and healthy fats, reflects a balanced nutritional profile.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Analyzing the vitamin and mineral content helps us understand whether a meal provides essential nutrients that support overall health. For example, a colorful salad with leafy greens, vegetables, and fruits may offer a wide array of vitamins and minerals.
- Fiber Content: Analyzing the fiber content of a meal is crucial for digestive health and satiety. A meal high in fiber from sources like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can promote fullness and support digestive regularity.
- Antioxidants and Phytonutrients: Meals with a diverse range of colorful fruits and vegetables provide antioxidants and phytonutrients, which can help protect the body against oxidative stress.
Understanding Nutritional Weaknesses
- Empty Calories: Meals with excessive empty calories, like sugary snacks and processed foods, can hinder your bodybuilding progress. In-depth analysis will identify these sources of empty calories, enabling you to reduce or eliminate them from your diet.
- Unhealthy Fats: Trans fats, saturated fats, and excessive unhealthy fats can negatively impact your bodybuilding efforts. A thorough analysis will pinpoint sources of unhealthy fats, such as fried foods and processed snacks, helping you make informed choices.

- Processed and Refined Ingredients: Processed and refined ingredients, like white bread and sugary cereals, lack essential nutrients and often contain added sugars and unhealthy additives.
Macroscopic Imbalance in Workouts
Macroscopic imbalance in the context of workouts refers to the deliberate adjustment of your macronutrient ratios to meet specific fitness goals. Depending on your objectives, you can manipulate your macros to optimize performance and recovery.
- Energy for Intense Workouts: If you’re engaging in intense workouts or endurance activities, you may increase your carbohydrate intake to ensure you have the necessary energy to sustain your performance. This creates a macroscopic imbalance with a higher proportion of carbs in your diet.
- Muscle Recovery and Growth: For individuals focused on building muscle, protein becomes a central macro. You’ll emphasize a higher protein intake to support muscle repair and growth, resulting in a macroscopic imbalance with more protein than the other macronutrients.

Customizing Macro Ratios
The key to effective macroscopic imbalance is customization. Your unique fitness goals, workout intensity, and individual response to different diets will determine the optimal macro ratios for you. This may involve monitoring the percentage of daily calories coming from each macronutrient and adjusting as needed.
Monitoring Progress
To understand the impact of macroscopic imbalance on your workout performance, you can track changes in strength, endurance, recovery, and overall fitness. This data helps you refine your macros to best align with your goals.
Mindful Eating: A Holistic Approach to Nutrition
Mindful eating is an approach that involves paying full attention to the experience of eating. This practice encourages a deeper connection between your mind and body, promoting more intentional food choices.

Here’s why it’s crucial for workout enthusiasts:
- Enhanced Nutrient Absorption: When you savor your food and eat slowly, you allow your digestive system to function more effectively. This can lead to improved nutrient absorption, ensuring that your body receives the full benefit of the nutrients you consume.
- Better Control of Hunger and Satiety: Mindful eating helps you recognize true hunger and fullness cues. This prevents overeating and can be particularly useful for those striving to manage their weight or portion control.
- Reduced Emotional Eating: Many individuals turn to food as a way to cope with stress or emotions. Mindful eating helps you distinguish between physical hunger and emotional cravings, reducing the likelihood of emotional eating.
Portion Control: The Key to Balanced Nutrition
Portion control goes hand in hand with mindful eating and plays a crucial role in achieving your fitness and nutritional goals:
- Calorie Management: Portion control allows you to manage your calorie intake more effectively. This is essential whether you’re trying to shed excess pounds or maintain your current weight.
- Balanced Macronutrients: Proper portion control ensures that you have a balanced intake of macronutrients (carbs, protein, fats), aligning with your fitness goals, such as muscle gain or fat loss.
- Preventing Overeating: Large portions often lead to overconsumption, which can hinder your fitness progress. By controlling your portions, you reduce the risk of eating more than your body needs.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of your food intake and portion sizes, especially when you’re working toward specific fitness goals. This data will help you stay on track and make necessary adjustments to your diet.









