In a world often fixated on weight loss, the pursuit of healthy weight gain shines as a refreshing endeavor. Imagine a voyage where every step forward isn’t about shedding but feeling a sense of well-being. This is the heart of healthy weight gain – a journey that celebrates nourishing your body to its potential.
The number of fat cells in our bodies remains relatively constant after adolescence. Gaining weight makes fat cells bigger; losing weight makes them smaller. That’s why it’s crucial to start taking care of your weight when you’re younger. Additionally, individuals often mirror the eating behaviors of those they are around. This occurrence is called “social contagion”, where our friends or family can unknowingly impact what we choose to eat and how we eat. Do you know about the Yo-Yo Dieting Effect? It’s the repeated cycles of weight loss and regain that can make it harder to lose weight in the long run. The body might start resisting efforts to lose weight.

Healthy weight gain isn’t about mindlessly devouring whatever’s within reach – it’s about nurturing your body like a prized garden and tending to it with care. This involves letting go of wrong beliefs, setting smart goals, and moving ahead with patience and strong commitment.
But, let’s shatter the stigma right away – healthy weight gain isn’t code for boring or tasteless flavors. It’s about savoring foods packed with nutrients that make your body stronger determination.
Achieving Success: Establishing Your Goals for Gaining Weight
- Define Your Goals: Start by clearly defining your weight gain goals. How much weight are you looking to add, and over what duration? Be specific and realistic in your expectations.
- Determine Your Caloric Needs: Figure out your daily calorie needs by considering your basic metabolism, how active you are, and your goal. This gives you a starting point for your eating plan.
- Plan Your Nutrition: Create a well-rounded and nutrient-packed meal plan that matches your calorie requirements. Incorporate a range of whole foods abundant in protein, complex carbs, good fats, and essential nutrients.
- Choose Your Workouts: Design a structured workout routine that includes resistance training and cardiovascular exercise. Prioritize multi-joint exercises to boost muscle development and overall physical power.
- Set Short-Term and Long-Term Milestones: Break down your overall weight gain goal into smaller, achievable milestones. For example, aim to gain a certain amount of weight per month or increase your strength on specific exercises.
- Monitor Progress: Track your weight, measurements, and workout performance regularly. Keep track of your progress using a journal, app, or spreadsheet.
- Stay Consistent and Patient: Consistency is key to achieving your weight gain goals. Stick to your routine, even when you face tough days.
- Seek Support and Guidance: Consider working with a registered dietitian, nutritionist, or personal trainer. Their expertise can provide valuable insights and keep you on track.
The Role Of Nutrition In Healthy Weight Gain
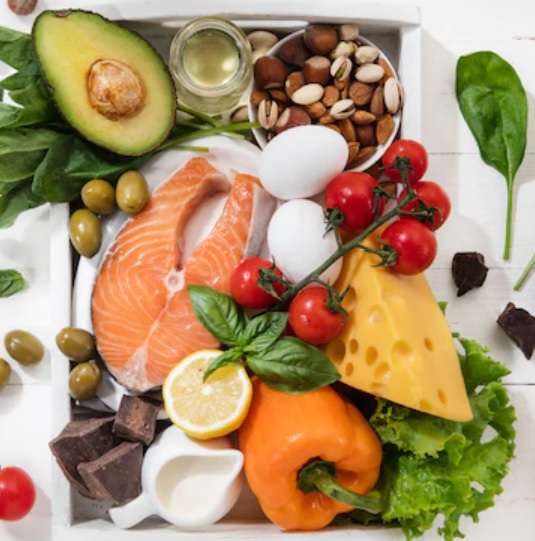
For a healthy weight gain, you need to consider the role of nutrition. Much like a well-oiled machine, your body requires a carefully balanced blend of nutrients to support optimal growth and development.
- Caloric Equilibrium: Consider calories as the fuel that powers your bodily functions and activities. However, it’s crucial to emphasize quality over quantity. Choosing calorie-rich foods that are packed with nutrients guarantees your body gets energy and important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Protein’s Fundamental Contribution: Protein plays an important role in supporting healthy weight gain, particularly in its function as the building block for muscle tissue. Foods rich in protein, such as lean meats, beans, and dairy products, contribute to muscle growth and repair.
- The Role of Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates, often not fully understood, are a vital energy source for your body. Choosing complex carbs from whole grains, fruits, and veggies gives you lasting energy, supporting steady nourishment.
- The Value of Healthy Fats: Healthy fats contribute more than flavor to your diet – they play an essential role in maintaining overall well-being. They are essential for cellular function and nutrient absorption. Incorporating sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil ensures a balanced intake of beneficial fats.
- Micronutrients: Vitamins and minerals, though required in smaller quantities, are no less important. These micronutrients support various bodily functions, from immune response to energy production. Ensuring a diverse and balanced diet helps guarantee an adequate supply of these essential elements.
- Hydration’s Understated Impact: Proper hydration is often underestimated but remains vital to your weight gain journey. Staying hydrated supports digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall bodily functions.
- Portion Control and Frequency: How you consume your meals can significantly impact your weight gain progress. Opting for balanced, smaller meals spread throughout the day helps maintain stable energy levels which can support your objective.
Understanding the Concept of a Caloric Surplus
- Calories In vs. Calories Out Weight gain and loss are fundamentally determined by the balance between calories consumed (calories in) and calories burned (calories out). If you consistently consume more calories than your body burns, you’ll create a caloric surplus.
- Energy Balance: To gain weight healthily, it’s important to create a modest caloric surplus rather than drastically overeating. This permits gradual weight gain, emphasizing muscle development instead of excessive fat increase.
- Muscle Growth: A caloric surplus provides your body with the necessary energy to repair and build new muscle tissue. When you engage in resistance training (weight lifting or bodyweight exercises), your muscles undergo microscopic damage that is repaired and reinforced during the recovery process. This leads to muscle growth and increased strength.
- Gradual Progression: Healthy weight gain should occur gradually, aiming for around 0.5 to 1 pound (0.2 to 0.45 kilograms) per week. This gives your body time to adapt and reduces the chance of gaining too much fat.
Strategic Snacking
- Additional Calories: Healthy snacks provide an opportunity to increase your daily caloric intake in a controlled manner. If you’re aiming for weight gain, taking slightly more calories than your body burns is essential.
- Sustained Energy: Well-balanced snacks that include a mix of protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates can provide sustained energy throughout the day. This can be particularly great for active individuals involved in workouts or physically demanding activities.
- Preventing Muscle Catabolism: When you go long periods without eating, your body can start breaking down muscle tissue for energy. Snacking between meals can help prevent this muscle catabolism.
Irresistible Power Snacks for Energy Boost
– Greek yogurt with fruit and nuts.
– Hummus with whole-grain crackers and carrot sticks.
– Cottage cheese with sliced avocado.
– Nut butter on whole-grain bread or rice cakes.
– Trail mix with dried fruits, nuts, and seeds.
– Hard-boiled eggs.
– Oatmeal with protein powder and berries.
– Fresh fruit with cheese.
– Veggie sticks with guacamole or salsa.

The Connection between Strength Training and Weight Gain
- Strength training is muscle-challenging exercises like weightlifting, resistance bands, push-ups, and squats which help muscle growth and contribute to weight gain.
- For effective muscle growth and weight gain, a caloric surplus is essential—consuming more calories than used. Engaging in strength training initiates muscle repair and building, demanding additional energy. This creates healthy weight gain, mainly lean muscle instead of excess fat.
- Engaging in strength training triggers the release of hormones like testosterone and growth hormone, which are important for building muscles.
- An important part of strength training is progressive overload. This means you gradually increase the resistance (weight) you lift over time. Continuously challenging your muscles with heavier weights stimulates muscle growth, resulting in weight gain.

Strategies for Overcoming Plateaus
Reevaluate Your Caloric Intake: If your weight gain has stalled, it’s possible that your caloric intake needs to be adjusted. If you’re not seeing weight gain, think about adding a bit more calories (like 100-200 calories a day) to create a surplus in your calorie intake.
- Modify Macronutrient Ratios: Adjusting your macronutrient ratios, particularly increasing your protein intake, can support muscle growth and recovery.
- Vary Your Workouts: Introduce new exercises, change your workout routine, or increase the intensity of your workouts. Your body can adapt to repetitive routines, leading to diminished progress.
- Change Rep and Set Schemes: Alter the number of sets, reps, and rest periods in your workouts. This variation can stimulate new muscle growth and challenge your body in different ways.
- Focus on Compound Movements: Emphasize compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups. These exercises are more effective for promoting overall muscle growth and strength.
- Address Recovery and Sleep: Ensure you’re getting enough sleep and allowing good time for recovery between workouts. Sleep is crucial for muscle repair.
- Stay Patient and Persistent: Plateaus are a normal part of any fitness journey. Stay patient and committed to your goals.
- Avoid Drastic Changes: While it’s important to make adjustments, avoid making drastic changes all at once. Gradual modifications are more sustainable and manageable.
- Psychological Factors: Stay positive and focused. Sometimes, mental barriers can contribute to plateaus. Reevaluate your mindset and motivation.
Supplements in Supporting Weight Gain
- Protein Supplements: Protein shakes, powders, or bars can help people meet their protein needs, which is crucial for muscle growth and repair.
- Weight Gainers: Weight gainer supplements are particularly useful for people struggling to have enough calories through whole foods alone.
- Creatine: Creatine is a well-researched supplement that may enhance muscle strength and power during resistance training, which can help create muscle mass.
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): BCAAs play a role in muscle protein synthesis and can help reduce muscle breakdown during intense workouts.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and can indirectly contribute to better workout recovery and muscle growth.
- Pre-Workout Supplements: Pre-workout supplements often contain ingredients like caffeine, which can enhance energy levels and focus during workouts, potentially leading to improved performance.
- Important Considerations: Always consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements. Supplements should complement a balanced diet, not replace it. Whole foods offer a diverse range of nutrients and health advantages that supplements cannot offer.
Avoiding Unhealthy Habits
Healthily gaining weight holds profound significance for overall well-being. It’s a journey that goes beyond just numbers on a scale, focusing on nurturing your body with balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and mindful habits. By focusing on slow and managed weight gain, you set the stage for lasting outcomes that are more likely to endure over time. This approach fosters the growth of lean muscle mass, which not only enhances your physical strength and functional abilities but also contributes to an improved metabolic profile.
Common Misconceptions about Weight Gain
- All Weight Gain is Unhealthy: Contrary to this belief, healthy weight gain involves gaining lean muscle mass rather than just fat.
- Eating Anything Will Lead to Weight Gain: Quality matters as much as quantity. Choosing nutrient-dense foods over empty calories is crucial for healthy weight gain. Overindulging in unhealthy foods can lead to undesired outcomes.
- Skipping Meals Helps Gain Weight: Skipping meals may lead to nutrient deficiencies and hinder weight gain efforts.
- Excessive Protein Leads to Rapid Muscle Gain: While protein is essential for muscle growth, excessive consumption won’t necessarily accelerate the process.
- Weight Gain Supplements Are the Shortcut: Supplements should complement a healthy diet, not replace it. Relying solely on supplements without proper nutrition and exercise may lead to imbalanced results.
- Gaining Weight Means Sacrificing Health: Gaining weight doesn’t inherently equate to sacrificing health. Concentrating on healthy foods and consistent exercise benefits both weight gain and overall health.
- More Calories, Faster Results: Rapidly increasing calorie intake can lead to excessive fat gain rather than muscle. Gradual caloric surplus combined with exercise promotes lean muscle growth.
- Strength Training Makes Women Bulky: Strength training can enhance muscle tone and metabolism without causing bulky muscles in women. It’s an essential component of healthy weight gain.
Gradual vs. Rapid Weight Gain: Pros and Cons
Gradual Weight Gain: Pros
- Healthier Body Composition: Slow and steady weight gain promotes muscle development, leading to a more balanced and aesthetically pleasing body composition.
- Healthy Eating Habits: Slow weight gain promotes the formation of lasting eating habits, nurturing a better connection with food.
- Long-Term Maintenance: Slow weight gain is often easier to maintain over the long term, preventing the need for constant fluctuations in diet and exercise.
Gradual Weight Gain: Cons
- Patience Required: Achieving results through gradual weight gain requires patience and consistent effort, which may be challenging for individuals seeking quick transformations.
- Psychological Impact: Progress might not be as visually apparent initially, potentially affecting motivation and self-esteem.
Rapid Weight Gain: Pros
- Quick Transformation: Rapid weight gain can lead to more immediate changes in body size and shape, which can be gratifying for those seeking swift results.
- Increased Caloric Intake: Rapid weight gain may allow for a higher caloric intake, which can be appealing to individuals with high metabolism or significant calorie needs.
Rapid Weight Gain: Cons
- Risk of Excessive Fat Gain: Rapid weight gain increases the likelihood of accumulating excess body fat, which may lead to negative health implications.
- Stretch Marks and Loose Skin: Rapid changes can stress the skin, leading to stretch marks or loose skin, especially if weight is gained too quickly.
- Potential Health Risks: Rapid weight gain can strain the cardiovascular system, impact blood sugar levels, and increase the risk of metabolic issues.
Choosing between gradual and rapid weight gain depends on individual goals, preferences, and overall health considerations. Striking a balance between achieving results and maintaining long-term well-being is essential for a successful weight gain journey.
Lean to Strong: Inspiring Stories
- Chris Pratt: Known for his role in “Guardians of the Galaxy,” Chris Pratt underwent a remarkable transformation from a lean sitcom actor to a muscular action star. He teamed up with trainers and nutrition experts, followed a strict exercise plan that involved building strength and cardio, and made big adjustments to his eating habits. This not only changed how he looked but also made him feel more confident and better overall.
- Zac Efron: Zac Efron transitioned from his lean teenage heartthrob image to a more muscular and athletic physique for roles like “Baywatch.” He followed a strict workout regimen that included heavy lifting, functional training, and intense outdoor activities. His dedication to fitness and nutrition allowed him to achieve a strong and shredded look.
- Jennifer Aniston: Jennifer Aniston, known for her role in “Friends,” transformed her physique over the years by incorporating regular strength training and yoga into her routine. Her dedication to staying active and embracing a balanced lifestyle has contributed to her strong and toned look.
Frequently Asked Questions: FAQs
How can I avoid excessive fat gain during weight gain?
Prioritize strength training to build lean muscle mass, which can help prevent excessive fat accumulation and contribute to a balanced physique.
Will strength training make me bulk up?
No, strength training won’t necessarily make you bulk up. It encourages the growth of lean muscles and defines look while also improving the body’s overall metabolism.
Can genetics affect my ability to gain weight?
Yes, genetics can influence your body’s tendency to store fat or build muscle. However, lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise also play a significant role.
Can I gain weight without exercising?
While exercise can support healthy weight gain and muscle development, focusing solely on diet can lead to undesired fat gain. Incorporating physical activity is recommended.
Is it possible to target weight gain to specific areas of the body?
Spot-targeted weight gain is generally not effective. A well-rounded strategy involving proper nutrition and exercise is more effective for overall weight gain.
Is weight gain linked to health problems?
Gaining too much weight, especially with unhealthy habits can increase the risk of health problems like heart disease, diabetes, and joint issues.
Will gaining weight affect my self-esteem?
Gaining weight might affect how you see yourself, but concentrating on good health, strength, and a positive body image can support a healthy self-view.










